Current approaches of the management of mercury poisoning: need of the hour
- PMID: 24888360
- PMCID: PMC4055906
- DOI: 10.1186/2008-2231-22-46
Current approaches of the management of mercury poisoning: need of the hour
Abstract
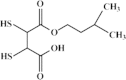
Mercury poisoning cases have been reported in many parts of the world, resulting in many deaths every year. Mercury compounds are classified in different chemical types such as elemental, inorganic and organic forms. Long term exposure to mercury compounds from different sources e.g. water, food, soil and air lead to toxic effects on cardiovascular, pulmonary, urinary, gastrointestinal, neurological systems and skin. Mercury level can be measured in plasma, urine, feces and hair samples. Urinary concentration is a good indicator of poisoning of elemental and inorganic mercury, but organic mercury (e.g. methyl mercury) can be detected easily in feces. Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) are a rapid, cheap and sensitive method for detection of thymine bound mercuric ions. Silver nanoparticles are used as a sensitive detector of low concentration Hg2+ ions in homogeneous aqueous solutions. Besides supportive therapy, British anti lewisite, dimercaprol (BAL), 2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA. succimer) and dimercaptopropanesulfoxid acid (DMPS) are currently used as chelating agents in mercury poisoning. Natural biologic scavengers such as algae, azolla and other aquatic plants possess the ability to uptake mercury traces from the environment.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Inorganic mercury poisoning associated with skin-lightening cosmetic products.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2011 Dec;49(10):886-91. doi: 10.3109/15563650.2011.626425. Epub 2011 Nov 9. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2011. PMID: 22070559 Review.
-
The role of chelation in the treatment of arsenic and mercury poisoning.J Med Toxicol. 2013 Dec;9(4):347-54. doi: 10.1007/s13181-013-0344-5. J Med Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 24178900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mercury binding to the chelation therapy agents DMSA and DMPS and the rational design of custom chelators for mercury.Chem Res Toxicol. 2004 Aug;17(8):999-1006. doi: 10.1021/tx049904e. Chem Res Toxicol. 2004. PMID: 15310232
-
[Metal poisoning].An Sist Sanit Navar. 2003;26 Suppl 1:141-53. An Sist Sanit Navar. 2003. PMID: 12813482 Review. Spanish.
-
Treatment of mercury intoxication.Curr Opin Pediatr. 1999 Jun;11(3):265-8. doi: 10.1097/00008480-199906000-00018. Curr Opin Pediatr. 1999. PMID: 10349108 Review.
Cited by
-
Metalloproteomic Investigation of Hg-Binding Proteins in Renal Tissue of Rats Exposed to Mercury Chloride.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 21;25(1):164. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010164. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203335 Free PMC article.
-
Laparoscopic appendectomy for elemental mercury sequestration in the appendix: A case report.World J Clin Cases. 2019 May 6;7(9):1038-1042. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i9.1038. World J Clin Cases. 2019. PMID: 31123676 Free PMC article.
-
Full Atrioventricular Block Secondary to Acute Poisoning Mercury: A Case Report.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018 Apr 2;15(4):657. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15040657. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018. PMID: 29614795 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms Mediating Methylmercury Neurotoxicity and Neuroinflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 18;22(6):3101. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063101. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33803585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peritonitis Due to Appendicitis Related to Mercury Sequestration: An Unusual Peruvian Case Report.Cureus. 2022 Aug 4;14(8):e27667. doi: 10.7759/cureus.27667. eCollection 2022 Aug. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36134106 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stwertka AA. A Guide to the Elements. 2. Oxford: Oxford University Press;
-
- Rafati-Rahimzadeh M, Moghaddamnia AA. Organophosphorus compounds poisoning. J Babol Univ Med Sci. 2010;12:71–85. [in Persian]
-
- Moghadamnia AA. Survey of acute suicidal poisoning in the west of Mazandaran province during the years 1994-97. J Mazandaran Univ Med Sci. 1999;22–23:18–25. [in Persian]
-
- Moghadamnia AA, Abdollahi M. An epidemiological study of poisoning in northern Islamic Republic of Iran. East Mediterr Health J. 2002;8:88–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

