Synergism and rules of the new combination drug Yiqijiedu formulae (YQJD) on ischemic stroke based on amino acids (AAs) metabolism
- PMID: 24889025
- PMCID: PMC4042126
- DOI: 10.1038/srep05149
Synergism and rules of the new combination drug Yiqijiedu formulae (YQJD) on ischemic stroke based on amino acids (AAs) metabolism
Abstract
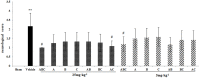
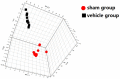
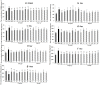
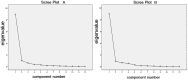
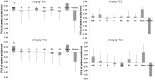
The use of combination drugs is considered to be a promising strategy to control complex diseases such as ischemic stroke. The detection of metabolites has been used as a versatile tool to reveal the potential mechanism of diverse diseases. In this study, the levels of 12 endogenous AAs were simultaneously determined quantitatively in the MCAO rat brain using RRLC-QQQ method. Seven AAs were chosen as the potential biomarkers, and using PLS-DA analysis, the effects of the new combination drug YQJD, which is composed of ginsenosides, berberine, and jasminoidin, on those 7 AAs were evaluated. Four AAs, glutamic acid, homocysteine, methionine, and tryptophan, which changed significantly in the YQJD-treated groups compared to the vehicle groups (P < 0.05), were identified and designated as the AAs to use to further explore the synergism of YQJD. The result of a PCA showed that the combination of these three drugs exhibits the strongest synergistic effect compared to other combination groups and that ginsenosides might play a pivotal role, especially when combined with jasminoidin. We successfully explored the synergetic mechanism of multi-component and provided a new method for evaluating the integrated effects of combination drugs in the treatment of complex diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Strong K., Mathers C. & Bonita R. Preventing stroke: saving lives around the world. Lancet Neurol. 6, 182–187 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Lloyd-Jones D. et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2009 update. A report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 119, e21–e181 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Brindle J. T. et al. Rapid and noninvasive diagnosis of the presence and severity of coronary heart disease using 1 H-NMR based metabonomics. NAT. MED. 8, 1439–1444 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

