Insulin receptor antibody-iduronate 2-sulfatase fusion protein: pharmacokinetics, anti-drug antibody, and safety pharmacology in Rhesus monkeys
- PMID: 24889100
- PMCID: PMC4176522
- DOI: 10.1002/bit.25289
Insulin receptor antibody-iduronate 2-sulfatase fusion protein: pharmacokinetics, anti-drug antibody, and safety pharmacology in Rhesus monkeys
Abstract
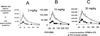
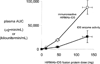
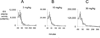
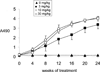
Mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS) Type II is caused by mutations in the gene encoding the lysosomal enzyme, iduronate 2-sulfatase (IDS). The majority of MPSII cases affect the brain. However, enzyme replacement therapy with recombinant IDS does not treat the brain, because IDS is a large molecule drug that does not cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB). To enable BBB penetration, IDS has been re-engineered as an IgG-IDS fusion protein, where the IgG domain is a monoclonal antibody (MAb) against the human insulin receptor (HIR). The HIRMAb crosses the BBB via receptor-mediated transport on the endogenous BBB insulin receptor, and the HIRMAb domain of the fusion protein acts as a molecular Trojan horse to ferry the fused IDS into brain from blood. The present study reports on the first safety pharmacology and pharmacokinetics study of the HIRMAb-IDS fusion protein. Juvenile male Rhesus monkeys were infused intravenously (IV) weekly for 26 weeks with 0, 3, 10, or 30 mg/kg of the HIRMAb-IDS fusion protein. The plasma clearance of the fusion protein followed a linear pharmacokinetics profile, which was equivalent either with measurements of the plasma concentration of immunoreactive HIRMAb-IDS fusion protein, or with assays of plasma IDS enzyme activity. Anti-drug antibody (ADA) titers were monitored monthly, and the ADA response was primarily directed against the variable region of the HIRMAb domain of the fusion protein. No infusion related reactions or clinical signs of immune response were observed during the course of the study. A battery of safety pharmacology, clinical chemistry, and tissue histopathology showed no signs of adverse events, and demonstrate the safety profile of chronic treatment of primates with 3-30 mg/kg weekly IV infusion doses of the HIRMAb-IDS fusion protein.
Keywords: blood-brain barrier; drug delivery; lysosomal enzyme; monoclonal antibody.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Expression in CHO cells and pharmacokinetics and brain uptake in the Rhesus monkey of an IgG-iduronate-2-sulfatase fusion protein.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2011 Aug;108(8):1954-64. doi: 10.1002/bit.23118. Epub 2011 Mar 15. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2011. PMID: 21351076 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-brain barrier molecular trojan horse enables imaging of brain uptake of radioiodinated recombinant protein in the rhesus monkey.Bioconjug Chem. 2013 Oct 16;24(10):1741-9. doi: 10.1021/bc400319d. Epub 2013 Oct 3. Bioconjug Chem. 2013. PMID: 24059813
-
IgG-enzyme fusion protein: pharmacokinetics and anti-drug antibody response in rhesus monkeys.Bioconjug Chem. 2013 Jan 16;24(1):97-104. doi: 10.1021/bc3005123. Epub 2012 Dec 31. Bioconjug Chem. 2013. PMID: 23249376 Free PMC article.
-
Reengineering biopharmaceuticals for targeted delivery across the blood-brain barrier.Methods Enzymol. 2012;503:269-92. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-396962-0.00011-2. Methods Enzymol. 2012. PMID: 22230573 Review.
-
Delivery of Biologics Across the Blood-Brain Barrier with Molecular Trojan Horse Technology.BioDrugs. 2017 Dec;31(6):503-519. doi: 10.1007/s40259-017-0248-z. BioDrugs. 2017. PMID: 29067674 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent trends in mucopolysaccharidosis research.J Hum Genet. 2019 Feb;64(2):127-137. doi: 10.1038/s10038-018-0534-8. Epub 2018 Nov 19. J Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 30451936 Review.
-
A Historical Review of Brain Drug Delivery.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jun 16;14(6):1283. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14061283. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35745855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Probing the brain with molecular fMRI.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2018 Jun;50:201-210. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2018.03.009. Epub 2018 Apr 9. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 29649765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Towards a translational physiologically-based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model for receptor-mediated transcytosis of anti-transferrin receptor monoclonal antibodies in the central nervous system.J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2022 Jun;49(3):337-362. doi: 10.1007/s10928-021-09800-w. Epub 2022 Jan 29. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2022. PMID: 35092540
-
Crossing the Blood-Brain Barrier: Innovations in Receptor- and Transporter-Mediated Transcytosis Strategies.Pharmaceutics. 2025 May 28;17(6):706. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17060706. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40574019 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Al Sawaf S, Mayatepek E, Hoffmann B. Neurological findings in Hunter disease: pathology and possible therapeutic effects reviewed. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2008;31:473–480. - PubMed
-
- Boado RJ, Hui EK-W, Lu JZ, Sumbria RK, Pardridge WM. Blood-brain barrier molecular Trojan horse enables brain imaging of radioiodinated recombinant protein in the Rhesus monkey. Bioconj Chem. 2013a;24:1741–1749. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

