Glial progenitors as targets for transformation in glioma
- PMID: 24889528
- PMCID: PMC4270964
- DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800249-0.00001-9
Glial progenitors as targets for transformation in glioma
Abstract
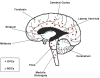
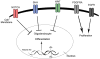
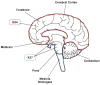
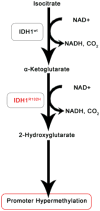
Glioma is the most common primary malignant brain tumor and arises throughout the central nervous system. Recent focus on stem-like glioma cells has implicated neural stem cells (NSCs), a minor precursor population restricted to germinal zones, as a potential source of gliomas. In this review, we focus on the relationship between oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPCs), the largest population of cycling glial progenitors in the postnatal brain, and gliomagenesis. OPCs can give rise to gliomas, with signaling pathways associated with NSCs also playing key roles during OPC lineage development. Gliomas can also undergo a switch from progenitor- to stem-like phenotype after therapy, consistent with an OPC-origin even for stem-like gliomas. Future in-depth studies of OPC biology may shed light on the etiology of OPC-derived gliomas and reveal new therapeutic avenues.
Keywords: Brain; Cancer; Glioblastoma; Glioma; Neural stem cell; Oligodendrocyte progenitor cell.
© 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Abel TW, Clark C, Bierie B, Chytil A, Aakre M, Gorska A, Moses HL. GFAP-Cre-mediated activation of oncogenic K-ras results in expansion of the subventricular zone and infiltrating glioma. Molecular cancer research MCR. 2009;7:645–653. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19435821. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aguilar-Morante D, Cortes-Canteli M, Sanz-Sancristobal M, Santos A, Perez-Castillo A. Decreased CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β expression inhibits the growth of glioblastoma cells. Neuroscience. 2011;176:110–119. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U54 CA163155/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA159859/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA82103/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54CA163155/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA176287/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA159859/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R25 GM055052/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA148699/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA102321/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA81403/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA133091/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA163155/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA082103/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

