Synaptic function of nicastrin in hippocampal neurons
- PMID: 24889619
- PMCID: PMC4066509
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1408554111
Synaptic function of nicastrin in hippocampal neurons
Abstract
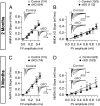
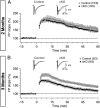
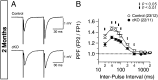
Synaptic dysfunction is widely thought to play a key role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Presenilins, the major gene products involved in familial AD, are essential for short- and long-term synaptic plasticity in mature neurons as well as for the survival of cortical neurons during aging. Presenilin and nicastrin are both indispensable components of the γ-secretase complex, but it remains unknown whether presenilin regulates synaptic function in a γ-secretase-dependent or γ-secretase-independent manner and whether nicastrin plays similar roles in central synapses. In the current study, we address these questions using an electrophysiological approach to analyze nicastrin conditional knockout (cKO) mice in the hippocampal Schaffer collateral pathway. In these mice, we found that, even at 2 mo of age, deletion of nicastrin in excitatory neurons of the postnatal forebrain using Cre recombinase expressed under the control of the αCaMKII promoter led to deficits in presynaptic short-term plasticity including paired-pulse facilitation and frequency facilitation. Depletion of Ca(2+) in the endoplasmic reticulum mimics and occludes the presynaptic facilitation deficits in nicastrin cKO mice, suggesting that disrupted intracellular Ca(2+) homeostasis underlies the presynaptic deficits. In addition, NMDA receptor-mediated responses and long-term potentiation induced by theta-burst stimulation were decreased in nicastrin cKO mice at 3 mo but not at 2 mo of age. Together, these findings show that, similar to presenilins, nicastrin plays essential roles in the regulation of short- and long-term synaptic plasticity, highlighting the importance of γ-secretase in the function of mature synapses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Presenilins regulate synaptic plasticity and mitochondrial calcium homeostasis in the hippocampal mossy fiber pathway.Mol Neurodegener. 2017 Jun 15;12(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s13024-017-0189-5. Mol Neurodegener. 2017. PMID: 28619096 Free PMC article.
-
Presenilins regulate synaptic plasticity in the perforant pathways of the hippocampus.Mol Brain. 2023 Jan 30;16(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13041-023-01009-x. Mol Brain. 2023. PMID: 36710361 Free PMC article.
-
Presenilins are essential for regulating neurotransmitter release.Nature. 2009 Jul 30;460(7255):632-6. doi: 10.1038/nature08177. Nature. 2009. PMID: 19641596 Free PMC article.
-
Function and dysfunction of presenilin.Neurodegener Dis. 2014;13(2-3):61-3. doi: 10.1159/000354971. Epub 2013 Oct 2. Neurodegener Dis. 2014. PMID: 24107444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Presenilins in synaptic function and disease.Trends Mol Med. 2011 Nov;17(11):617-24. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2011.06.002. Epub 2011 Jul 26. Trends Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21795114 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Presenilin-1 knockin mice reveal loss-of-function mechanism for familial Alzheimer's disease.Neuron. 2015 Mar 4;85(5):967-81. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.02.010. Neuron. 2015. PMID: 25741723 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary proteome profiling for children with autism using data-independent acquisition proteomics.Transl Pediatr. 2021 Jul;10(7):1765-1778. doi: 10.21037/tp-21-193. Transl Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34430425 Free PMC article.
-
An Evolutionarily Conserved Role of Presenilin in Neuronal Protection in the Aging Drosophila Brain.Genetics. 2017 Jul;206(3):1479-1493. doi: 10.1534/genetics.116.196881. Epub 2017 May 11. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28495961 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping dynamic molecular changes in hippocampal subregions after traumatic brain injury through spatial proteomics.Clin Proteomics. 2024 May 12;21(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s12014-024-09485-6. Clin Proteomics. 2024. PMID: 38735925 Free PMC article.
-
The genes associated with early-onset Alzheimer's disease.Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 15;9(19):15132-15143. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23738. eCollection 2018 Mar 13. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29599933 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yu G, et al. Nicastrin modulates presenilin-mediated notch/glp-1 signal transduction and betaAPP processing. Nature. 2000;407(6800):48–54. - PubMed
-
- Li J, et al. Positive and negative regulation of the gamma-secretase activity by nicastrin in a murine model. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(35):33445–33449. - PubMed
-
- Shen J, et al. Skeletal and CNS defects in Presenilin-1-deficient mice. Cell. 1997;89(4):629–639. - PubMed
-
- Wong PC, et al. Presenilin 1 is required for Notch1 and DII1 expression in the paraxial mesoderm. Nature. 1997;387(6630):288–292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

