Rapid antimicrobial susceptibility testing with electrokinetics enhanced biosensors for diagnosis of acute bacterial infections
- PMID: 24889716
- PMCID: PMC4206609
- DOI: 10.1007/s10439-014-1040-6
Rapid antimicrobial susceptibility testing with electrokinetics enhanced biosensors for diagnosis of acute bacterial infections
Abstract
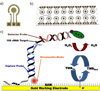
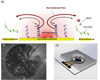
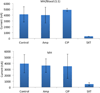
Rapid pathogen detection and antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) are required in diagnosis of acute bacterial infections to determine the appropriate antibiotic treatment. Molecular approaches for AST are often based on the detection of known antibiotic resistance genes. Phenotypic culture analysis requires several days from sample collection to result reporting. Toward rapid diagnosis of bacterial infection in non-traditional healthcare settings, we have developed a rapid AST approach that combines phenotypic culture of bacterial pathogens in physiological samples and electrochemical sensing of bacterial 16S rRNA. The assay determines the susceptibility of pathogens by detecting bacterial growth under various antibiotic conditions. AC electrokinetic fluid motion and Joule heating induced temperature elevation are optimized to enhance the sensor signal and minimize the matrix effect, which improve the overall sensitivity of the assay. The electrokinetics enhanced biosensor directly detects the bacterial pathogens in blood culture without prior purification. Rapid determination of the antibiotic resistance profile of Escherichia coli clinical isolates is demonstrated.
Figures




References
-
- Pinner RW, Teutsch SM, Simonsen L, Klug LA, Graber JM, Clarke MJ, Berkelman RL. Trends in infectious diseases mortality in the united states. Jama-Journal of the American Medical Association. 1996;275:189–193. - PubMed
-
- Hawkey PM. Pre-clinical experience with daptomycin. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008;62:7–14. - PubMed
-
- Daum RS, Ito T, Hiramatsu K, Hussain F, Mongkolrattanothai K, Jamklang M, Boyle-Wang S. A novel methicillin-resistance cassette in community-acquired methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus isolates of diverse genetic backgrounds. J. Infect. Dis. 2002;186:1344–1347. - PubMed
-
- Herold BC, Immergluck LC, Maranan MC, Lauderdale DS, Gaskin RE, Boyle-Vavra S, Leitch CD, Daum RS. Community-acquired methicillinresistant staphylococcus aureus in children with no identified predisposing risk. Jama-Journal of the American Medical Association. 1998;279:593–598. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

