Apoptosis of alcohol-exposed human placental cytotrophoblast cells is downstream of intracellular calcium signaling
- PMID: 24889927
- PMCID: PMC4049269
- DOI: 10.1111/acer.12417
Apoptosis of alcohol-exposed human placental cytotrophoblast cells is downstream of intracellular calcium signaling
Abstract
Background: Apoptosis is induced by ethanol (EtOH) in human placental trophoblast cells, possibly disrupting placentation and contributing to intrauterine growth restriction in fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD). EtOH induces programmed cell death in several embryonic tissues by raising intracellular Ca(2+) . Therefore, the role of Ca(2+) signaling in EtOH-induced apoptosis was examined using human first trimester cytotrophoblast cell lines, examining the hypothesis that apoptosis is dependent on intracellular Ca(2+) signaling.
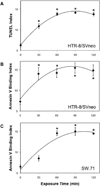
Methods: Using HTR-8/SVneo and SW.71 cytotrophoblast cell lines, real-time intracellular Ca(2+) concentration was monitored by fluo-4 epifluorescence microscopy and apoptosis was assessed by flow cytometry of cells fluorescently labeled for DNA fragmentation (TUNEL) and annexin V binding.
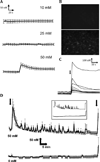
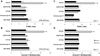
Results: Intracellular Ca(2+) concentrations increased synchronously in all cells within 10 seconds of exposure to 50 mM EtOH, but not at lower EtOH concentrations (10 to 25 mM) incapable of inducing apoptosis. Trophoblast cells treated with inhibitors of Ca(2+) signaling (BAPTA-AM, U73122, xestospongin D, BAPTA, SKF-96365) produced no intracellular Ca(2+) transients after exposure to 50 mM EtOH and were protected from cell death induced by EtOH.
Conclusions: EtOH-induced apoptosis in human cytotrophoblast cells, identified by DNA fragmentation and externalized phosphatidylserine, was dependent upon Ca(2+) signaling. Both intracellular Ca(2+) mobilization and extracellular Ca(2+) influx were required, as well as phosphatidylinositol signaling. Inhibition by SKF-96365 suggests that the capacitative Ca(2+) entry mechanism that utilizes TRPC channels was activated by EtOH. Apoptosis occurs downstream of Ca(2+) signaling in trophoblasts and may contribute to placental insufficiency and poor fetal growth associated with FASD.
Keywords: Alcohol; Apoptosis; Calcium; Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder; Intracellular Signaling; Intrauterine Growth Restriction; Trophoblast.
Copyright © 2014 by the Research Society on Alcoholism.
Figures

References
-
- Axt R, Kordina AC, Meyberg R, Reitnauer K, Mink D, Schmidt W. Immunohistochemical evaluation of apoptosis in placentae from normal and intrauterine growth-restricted pregnancies. Clin.Exp.Obstet.Gynecol. 1999;26:195–198. - PubMed
-
- Barrio E, Calvo MT, Romo A, Alvarez R, Gutierrez JI, Naval J, Ferrandez LA. Intrauterine growth retardation: study of placental apoptosis. J.Pediatr.Endocrinol.Metab. 2004;17(Suppl 3):451–456. - PubMed
-
- Carvou N, Norden AG, Unwin RJ, Cockcroft S. Signalling through phospholipase C interferes with clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Cell Signal. 2007;19:42–51. - PubMed
-
- De A, Boyadjieva NI, Sarkar DK. Effect of voltage-dependent calcium channel blockers on ethanol-induced beta-endorphin release from hypothalamic neurons in primary cultures. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1999;23:850–855. - PubMed
-
- Debelak-Kragtorp KA, Armant DR, Smith SM. Ethanol-induced cephalic apoptosis requires phospholipase C-dependent intracellular calcium signaling. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2003;27:515–523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

