Glial cells suppress postencephalitic CD8+ T lymphocytes through PD-L1
- PMID: 24890099
- PMCID: PMC4141010
- DOI: 10.1002/glia.22701
Glial cells suppress postencephalitic CD8+ T lymphocytes through PD-L1
Abstract
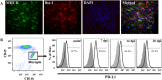
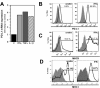
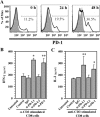
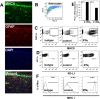
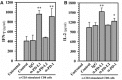
Engagement of the programmed death (PD)-1 receptor on activated cells by its ligand (PD-L1) is a mechanism for suppression of activated T-lymphocytes. Microglia, the resident inflammatory cells of the brain, are important for pathogen detection and initiation of innate immunity, however, a novel role for these cells as immune regulators has also emerged. PD-L1 on microglia has been shown to negatively regulate T-cell activation in models of multiple sclerosis and acute viral encephalitis. In this study, we investigated the role of glial cell PD-L1 in controlling encephalitogenic CD8(+) T-lymphocytes, which infiltrate the brain to manage viral infection, but remain to produce chronic neuroinflammation. Using a model of chronic neuroinflammation following murine cytomegalovirus (MCMV)-induced encephalitis, we found that CD8(+) T-cells persisting within the brain expressed PD-1. Conversely, activated microglia expressed PD-L1. In vitro, primary murine microglia, which express low basal levels of PD-L1, upregulated the co-inhibitory ligand on IFN-γ-treatment. Blockade of the PD-1: PD-L1 pathway in microglial: CD8(+) T-cell co-cultures increased T-cell IFN-γ and interleukin (IL)-2 production. We observed a similar phenomenon following blockade of this co-inhibitory pathway in astrocyte: CD8(+) T-cell co-cultures. Using ex vivo cultures of brain leukocytes, including microglia and CD8(+) T-cells, obtained from mice with MCMV-induced chronic neuroinflammation, we found that neutralization of either PD-1 or PD-L1 increased IFN-γ production from virus-specific CD8(+) T-cells stimulated with MCMV IE1168-176 peptide. These data demonstrate that microglia and astrocytes control antiviral T-cell responses and suggest a therapeutic potential of PD1: PD-L1 modulation to manage the deleterious consequences of uncontrolled neuroinflammation.
Keywords: astrocyte; encephalitis; immune suppression; major histocompatibility complex Class II; microglia; neuroinflammation.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Aloisi F. 2001. Immune function of microglia. Glia 36:165–179. - PubMed
-
- Blais V, Rivest S. 2004. Effects of TNF‐alpha and IFN‐gamma on nitric oxide‐induced neurotoxicity in the mouse brain. J Immunol 172:7043–7052. - PubMed
-
- Carter LL, Leach MW, Azoitei ML, Cui J, Pelker JW, Jussif J, Benoit S, Ireland G, Luxenberg D, Askew GR, KL Milarski, C Groves, T Brown, BA Carito, K Percival, BM Carreno, M Collins, S Marusic. 2007. PD‐1/PD‐L1, but not PD‐1/PD‐L2, interactions regulate the severity of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol 182:124–134. - PubMed
-
- Cheeran MC, Gekker G, Hu S, Min X, Cox D, Lokensgard JR. 2004. Intracerebral infection with murine cytomegalovirus induces CXCL10 and is restricted by adoptive transfer of splenocytes. J Neurovirol 10:152–162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

