Root exudation of phytosiderophores from soil-grown wheat
- PMID: 24890330
- PMCID: PMC4143957
- DOI: 10.1111/nph.12868
Root exudation of phytosiderophores from soil-grown wheat
Abstract
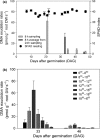
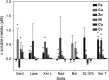
For the first time, phytosiderophore (PS) release of wheat (Triticum aestivum cv Tamaro) grown on a calcareous soil was repeatedly and nondestructively sampled using rhizoboxes combined with a recently developed root exudate collecting tool. As in nutrient solution culture, we observed a distinct diurnal release rhythm; however, the measured PS efflux was c. 50 times lower than PS exudation from the same cultivar grown in zero iron (Fe)-hydroponic culture. Phytosiderophore rhizosphere soil solution concentrations and PS release of the Tamaro cultivar were soil-dependent, suggesting complex interactions of soil characteristics (salinity, trace metal availability) and the physiological status of the plant and the related regulation (amount and timing) of PS release. Our results demonstrate that carbon and energy investment into Fe acquisition under natural growth conditions is significantly smaller than previously derived from zero Fe-hydroponic studies. Based on experimental data, we calculated that during the investigated period (21-47 d after germination), PS release initially exceeded Fe plant uptake 10-fold, but significantly declined after c. 5 wk after germination. Phytosiderophore exudation observed under natural growth conditions is a prerequisite for a more accurate and realistic assessment of Fe mobilization processes in the rhizosphere using both experimental and modeling approaches.
Keywords: 2′-deoxymugineic acid (DMA); Triticum aestivum cv Tamaro; iron deficiency; phytosiderophore; rhizosphere; strategy II; trace elements.
© 2014 The Authors. New Phytologist © 2014 New Phytologist Trust.
Figures


References
-
- Broadley M, Brown P, Cakmak I, Rengel Z, Zhao F. Chapter 7 – Function of nutrients: micronutrients. In: Marschner P, editor. Marschner's mineral nutrition of higher plants. 3rd edn. London, UK: Academic Press; 2012. pp. 191–248.
-
- Cakmak I, Gulut KY, Marschner H, Graham RD. Effect of zinc and iron deficiency on phytosiderophore release in wheat genotypes differing in zinc efficiency. Journal of Plant Nutrition. 1994;17:1–17.
-
- Chaignon V, Di Malta D, Hinsinger P. Fe-deficiency increases Cu acquisition by wheat cropped in a Cu-contaminated vineyard soil. New Phytologist. 2002;154:121–130.
-
- Charlson DV, Shoemaker RC. Evolution of iron acquisition in higher plants. Journal of Plant Nutrition. 2006;29:1109–1125.
-
- Clark RB, Römheld V, Marschner H. Iron uptake and phytosiderophore release by roots of sorghum genotypes1. Journal of Plant Nutrition. 1988;11:663–676.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

