Fractional factorial design to investigate stromal cell regulation of macrophage plasticity
- PMID: 24891120
- PMCID: PMC5928506
- DOI: 10.1002/bit.25282
Fractional factorial design to investigate stromal cell regulation of macrophage plasticity
Abstract
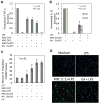
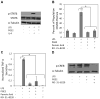
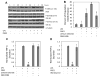
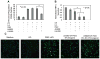
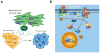
Understanding the regulatory networks which control specific macrophage phenotypes is essential in identifying novel targets to correct macrophage mediated clinical disorders, often accompanied by inflammatory events. Since mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) have been shown to play key roles in regulating immune functions predominantly via a large number of secreted products, we used a fractional factorial approach to streamline experimental evaluation of MSC mediated inflammatory macrophage regulation. Our macrophage reprogramming metrics, human bone marrow MSC attenuation of macrophage pro-inflammatory M1 TNFα secretion and simultaneous enhanced expression of the M2 macrophage marker, CD206, were used as analysis endpoints. Objective evaluation of a panel of MSC secreted mediators indicated that PGE2 alone was sufficient in facilitating macrophage reprogramming, while IL4 only provided partial reprogramming. Inhibiting stromal cell PGE2 secretion with Indomethacin, reversed the macrophage reprogramming effect. PGE2 reprogramming was mediated through the EP4 receptor and indirectly through the CREB signaling pathway as GSK3 specific inhibitors induced M1 macrophages to express CD206. This reprogramming pathway functioned independently from the M1 suppression pathway, as neither CREB nor GSK3 inhibition reversed PGE2 TNF-α secretion attenuation. In conclusion, fractional factorial experimental design identified stromal derived PGE2 as the factor most important in facilitating macrophage reprogramming, albeit via two unique pathways.
Keywords: PGE2; fractional factorial design; macrophage; mesenchymal stromal cells.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

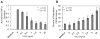
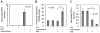
Similar articles
-
Preconditioning of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells highly strengthens their potential to promote IL-6-dependent M2b polarization.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018 Oct 25;9(1):286. doi: 10.1186/s13287-018-1039-2. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 30359316 Free PMC article.
-
Human mesenchymal stem/stromal cells cultured as spheroids are self-activated to produce prostaglandin E2 that directs stimulated macrophages into an anti-inflammatory phenotype.Stem Cells. 2012 Oct;30(10):2283-96. doi: 10.1002/stem.1191. Stem Cells. 2012. PMID: 22865689 Free PMC article.
-
Preconditioning of murine mesenchymal stem cells synergistically enhanced immunomodulation and osteogenesis.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017 Dec 6;8(1):277. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0730-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 29212557 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of IL-1β and LPS as optimal activators of monolayer and alginate-encapsulated mesenchymal stromal cell immunomodulation using design of experiments and statistical methods.Biotechnol Prog. 2015 Jul-Aug;31(4):1058-70. doi: 10.1002/btpr.2103. Epub 2015 May 28. Biotechnol Prog. 2015. PMID: 25958832 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cells Direct the Immunological Fate of Macrophages.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2017;62:61-72. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-54090-0_4. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2017. PMID: 28455706 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA Interference Screening Reveals Host CaMK4 as a Regulator of Cryptococcal Uptake and Pathogenesis.Infect Immun. 2017 Nov 17;85(12):e00195-17. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00195-17. Print 2017 Dec. Infect Immun. 2017. PMID: 28970273 Free PMC article.
-
Donor variability among anti-inflammatory pre-activated mesenchymal stromal cells.Technology (Singap World Sci). 2016 Sep;4(3):201-215. doi: 10.1142/S2339547816500084. Technology (Singap World Sci). 2016. PMID: 29732384 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia Impairs Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Induced Macrophage M1 to M2 Transition.Technology (Singap World Sci). 2017 Jun;5(2):81-86. doi: 10.1142/S2339547817500042. Technology (Singap World Sci). 2017. PMID: 29552603 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of local anesthetic on pro-inflammatory macrophage modulation by mesenchymal stromal cells.Int Immunopharmacol. 2016 Apr;33:48-54. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.01.019. Epub 2016 Feb 6. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26854576 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a microfluidic immunoassay capable of multiplexing parallel samples in microliter volumes.Lab Chip. 2015 Aug 7;15(15):3211-21. doi: 10.1039/c5lc00398a. Lab Chip. 2015. PMID: 26130452 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bullock BP, Habener JF. Phosphorylation of the cAMP response element binding protein CREB by cAMP-dependent protein kinase A and glycogen synthase kinase-3 alters DNA-binding affinity, conformation, and increases net charge. Biochemistry. 1998;37:3795–3809. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Bloemen V, Impens S, Moesen M, Luyten FP, Schrooten J. Characterization and optimization of cell seeding in scaffolds by factorial design: Quality by design approach for skeletal tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2011;17:1211–1221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

