Gibberellin biosynthesis and signal transduction is essential for internode elongation in deepwater rice
- PMID: 24891164
- PMCID: PMC4282320
- DOI: 10.1111/pce.12377
Gibberellin biosynthesis and signal transduction is essential for internode elongation in deepwater rice
Abstract
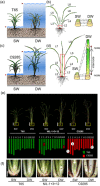
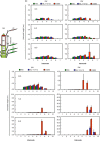
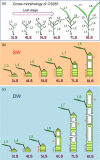
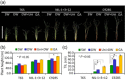
Under flooded conditions, the leaves and internodes of deepwater rice can elongate above the water surface to capture oxygen and prevent drowning. Our previous studies showed that three major quantitative trait loci (QTL) regulate deepwater-dependent internode elongation in deepwater rice. In this study, we investigated the age-dependent internode elongation in deepwater rice. We also investigated the relationship between deepwater-dependent internode elongation and the phytohormone gibberellin (GA) by physiological and genetic approach using a QTL pyramiding line (NIL-1 + 3 + 12). Deepwater rice did not show internode elongation before the sixth leaf stage under deepwater condition. Additionally, deepwater-dependent internode elongation occurred on the sixth and seventh internodes during the sixth leaf stage. These results indicate that deepwater rice could not start internode elongation until the sixth leaf stage. Ultra-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass-spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) method for the phytohormone contents showed a deepwater-dependent GA1 and GA4 accumulation in deepwater rice. Additionally, a GA inhibitor abolished deepwater-dependent internode elongation in deepwater rice. On the contrary, GA feeding mimicked internode elongation under ordinary growth conditions. However, mutations in GA biosynthesis and signal transduction genes blocked deepwater-dependent internode elongation. These data suggested that GA biosynthesis and signal transduction are essential for deepwater-dependent internode elongation in deepwater rice.
Keywords: gibberellin.
© 2014 The Authors. Plant, Cell & Environment published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures



References
-
- Asami T, Mizutani M, Fujioka S, Goda H, Min YK, Shimada Y. Yoshida S. Selective interaction of triazole derivatives with DWF4, a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase of the brassinosteroid biosynthetic pathway, correlates with brassinosteroid deficiency in planta. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2001;276:25687–25691. - PubMed
-
- Asano K, Hirano K, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Angeles-Shim RB, Komura T, Satoh H. Ashikari M. Isolation and characterization of dominant dwarf mutants, Slr1-d, in rice. Molecular Genetics and Genomics. 2009;281:223–231. - PubMed
-
- Catling HD. Rice in Deep Water. London: Macmillan [for the] International Rice Research Institute; 1992.
-
- Choi D. Ethylene-induced stem growth of deepwater rice is correlated with expression of gibberellin- and abscisic acid-biosynthetic genes. Journal of Plant Biology. 2007;50:595–599.
-
- Chomczynski P. Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Analytical Biochemistry. 1987;162:156–159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

