Enhanced lipid isomer separation in human plasma using reversed-phase UPLC with ion-mobility/high-resolution MS detection
- PMID: 24891331
- PMCID: PMC4109771
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.D047795
Enhanced lipid isomer separation in human plasma using reversed-phase UPLC with ion-mobility/high-resolution MS detection
Abstract
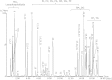
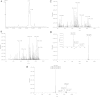
An ultraperformance LC (UPLC) method for the separation of different lipid molecular species and lipid isomers using a stationary phase incorporating charged surface hybrid (CSH) technology is described. The resulting enhanced separation possibilities of the method are demonstrated using standards and human plasma extracts. Lipids were extracted from human plasma samples with the Bligh and Dyer method. Separation of lipids was achieved on a 100 × 2.1 mm inner diameter CSH C18 column using gradient elution with aqueous-acetonitrile-isopropanol mobile phases containing 10 mM ammonium formate/0.1% formic acid buffers at a flow rate of 0.4 ml/min. A UPLC run time of 20 min was routinely used, and a shorter method with a 10 min run time is also described. The method shows extremely stable retention times when human plasma extracts and a variety of biofluids or tissues are analyzed [intra-assay relative standard deviation (RSD) <0.385% and <0.451% for 20 and 10 min gradients, respectively (n = 5); interassay RSD <0.673% and <0.763% for 20 and 10 min gradients, respectively (n = 30)]. The UPLC system was coupled to a hybrid quadrupole orthogonal acceleration time-of-flight mass spectrometer, equipped with a traveling wave ion-mobility cell. Besides demonstrating the separation for different lipids using the chromatographic method, we demonstrate the use of the ion-mobility MS platform for the structural elucidation of lipids. The method can now be used to elucidate structures of a wide variety of lipids in biological samples of different matrices.
Keywords: charge surface hybrid column; ion-mobility/high-resolution mass spectrometry; structural elucidation; ultraperformance liquid chromatography.
Copyright © 2014 by the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Ultrahigh-Performance capillary liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry at 35 kpsi for separation of lipids.J Chromatogr A. 2020 Jan 25;1611:460575. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2019.460575. Epub 2019 Sep 26. J Chromatogr A. 2020. PMID: 31607445 Free PMC article.
-
Novel application of reversed-phase UPLC-oaTOF-MS for lipid analysis in complex biological mixtures: a new tool for lipidomics.J Proteome Res. 2007 Feb;6(2):552-8. doi: 10.1021/pr060611b. J Proteome Res. 2007. PMID: 17269712
-
Rapid profiling method for the analysis of lipids in human plasma using ion mobility enabled-reversed phase-ultra high performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr A. 2020 Jan 25;1611:460597. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2019.460597. Epub 2019 Oct 4. J Chromatogr A. 2020. PMID: 31619360
-
Comprehensive two-dimensional separation of hydroxylated polybrominated diphenyl ethers by ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with ion mobility-mass spectrometry.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2011 Oct;22(10):1851-61. doi: 10.1007/s13361-011-0200-2. Epub 2011 Aug 16. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2011. PMID: 21952898
-
Validation and application of a high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometric method for simultaneous quantification of lopinavir and ritonavir in human plasma using semi-automated 96-well liquid-liquid extraction.J Chromatogr A. 2006 Oct 20;1130(2):302-7. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2006.07.071. Epub 2006 Aug 21. J Chromatogr A. 2006. PMID: 16919649
Cited by
-
Revealing Fatty Acid Heterogeneity in Staphylococcal Lipids with Isotope Labeling and RPLC-IM-MS.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2021 Sep 1;32(9):2376-2385. doi: 10.1021/jasms.1c00092. Epub 2021 May 20. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2021. PMID: 34014662 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinoma by high-definition mass spectrometry: Ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry and desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry imaging.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2020 Apr;34 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):e8551. doi: 10.1002/rcm.8551. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2020. PMID: 31412144 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating lipid mediator structural complexity using ion mobility spectrometry combined with mass spectrometry.Bioanalysis. 2018 Mar 1;10(5):279-289. doi: 10.4155/bio-2017-0245. Epub 2018 Mar 1. Bioanalysis. 2018. PMID: 29494212 Free PMC article.
-
Localization of Cyclopropane Modifications in Bacterial Lipids via 213 nm Ultraviolet Photodissociation Mass Spectrometry.Anal Chem. 2019 May 21;91(10):6820-6828. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b01038. Epub 2019 May 3. Anal Chem. 2019. PMID: 31026154 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in Mass Spectrometry-Based Targeted Metabolomics and Lipidomics: Implications for Clinical Research.Molecules. 2024 Dec 16;29(24):5934. doi: 10.3390/molecules29245934. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39770023 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Maxfield F. R., Tabas I. 2005. Role of cholesterol and lipid organization in disease. Nature. 438: 612–621. - PubMed
-
- Fahy E., Subramaniam S., Brown H. A., Glass C. K., Merrill A. H., Murphy R. C., Raetz C. R. H., Russell D. W., Seyama Y., Shaw W., et al. 2005. A comprehensive classification system for lipids. J. Lipid Res. 46: 839–861. - PubMed
-
- Spener F., Lagarde M., Géloên A., Record M. 2003. Editorial: what is lipidomics? Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 105: 481–482.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

