Direct transcriptional repression of Zfp423 by Zfp521 mediates a bone morphogenic protein-dependent osteoblast versus adipocyte lineage commitment switch
- PMID: 24891617
- PMCID: PMC4135594
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00185-14
Direct transcriptional repression of Zfp423 by Zfp521 mediates a bone morphogenic protein-dependent osteoblast versus adipocyte lineage commitment switch
Abstract
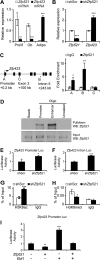
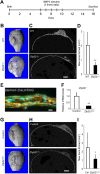
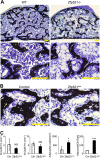
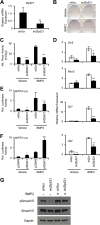
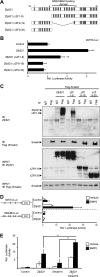
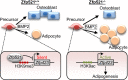
Osteoblasts and adipocytes arise from a common mesenchymal precursor cell. The cell fate decision of a mesenchymal precursor cell is under the influence of molecular cues and signaling pathways that lead to the activation or repression of lineage-specific transcription factors. The molecular mechanisms determining osteoblast versus adipocyte lineage specificity in response to bone morphogenic protein (BMP) remain unclear. In this study, we describe the mechanism through which Zfp521 (ZNF521), a regulator of lineage progression in multiple immature cell populations, regulates lineage specification of mesenchymal progenitor cells during BMP-induced differentiation events. In vivo deletion or in vitro knockdown of Zfp521 in mesenchymal precursors resulted in increased expression of the adipocyte determinant factor Zfp423 (ZNF423). This was concurrent with the loss of histone H3K9 methylation and an increase in histone H3K9 acetylation at the Zfp423 promoter, which together are indicative of decreased gene repression. Indeed, we found that Zfp521 occupies and represses the promoter and intronic enhancer regions of Zfp423. Accordingly, conditional deletion of Zfp521 inhibited heterotopic bone formation in response to local injection of BMP2. In contrast, marrow adiposity within BMP2-induced bone was markedly enhanced in Zfp521-deficient mice, suggesting that precursor cells lacking Zfp521 differentiate preferentially into adipocytes instead of osteoblasts in response to BMP2. Consistent with a cell-autonomous role of Zfp521 in mesenchymal precursors, knockdown of Zfp521 in stromal cells prevented BMP2-induced osteoblast marker expression and simultaneously enhanced lipid accumulation and expression of adipocyte-related genes. Taken together, the data suggest that Zfp521 is a cell fate switch critical for BMP-induced osteoblast commitment and identify Zfp521 as the intrinsic repressor of Zfp423 and hence of adipocyte commitment during BMP-induced mesenchymal precursor differentiation.
Copyright © 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epigenetic modifications of the Zfp/ZNF423 gene control murine adipogenic commitment and are dysregulated in human hypertrophic obesity.Diabetologia. 2018 Feb;61(2):369-380. doi: 10.1007/s00125-017-4471-4. Epub 2017 Oct 24. Diabetologia. 2018. PMID: 29067487 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of early adipose commitment by Zfp521.PLoS Biol. 2012;10(11):e1001433. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001433. Epub 2012 Nov 27. PLoS Biol. 2012. PMID: 23209378 Free PMC article.
-
Differential roles for bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) receptor type IB and IA in differentiation and specification of mesenchymal precursor cells to osteoblast and adipocyte lineages.J Cell Biol. 1998 Jul 13;142(1):295-305. doi: 10.1083/jcb.142.1.295. J Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9660882 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc finger protein 521, a new player in bone formation.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010 Mar;1192:32-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05347.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010. PMID: 20392215 Review.
-
PPARγ and Wnt Signaling in Adipogenic and Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;11(3):216-25. doi: 10.2174/1574888x10666150519093429. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 25986621 Review.
Cited by
-
Age-dependent genes in adipose stem and precursor cells affect regulation of fat cell differentiation and link aging to obesity via cellular and genetic interactions.Genome Med. 2024 Jan 31;16(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s13073-024-01291-x. Genome Med. 2024. PMID: 38297378 Free PMC article.
-
GCN5 modulates osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells through DKK1 acetylation in inflammatory microenvironment.Sci Rep. 2016 May 24;6:26542. doi: 10.1038/srep26542. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27216891 Free PMC article.
-
ZFP521 contributes to pre-B-cell lymphomagenesis through modulation of the pre-B-cell receptor signaling pathway.Oncogene. 2016 Jun 23;35(25):3227-38. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.385. Epub 2015 Nov 2. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26522721
-
Epigenetic Mechanisms Regulating Mesenchymal Stem Cell Differentiation.Curr Genomics. 2015 Dec;16(6):368-83. doi: 10.2174/1389202916666150817202559. Curr Genomics. 2015. PMID: 27019612 Free PMC article.
-
The stem cell-associated transcription co-factor, ZNF521, interacts with GLI1 and GLI2 and enhances the activity of the Sonic hedgehog pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Sep 26;10(10):715. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1946-x. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31558698 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
