Hesperidin inhibits inflammatory response induced by Aeromonas hydrophila infection and alters CD4+/CD8+ T cell ratio
- PMID: 24891765
- PMCID: PMC4033591
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/393217
Hesperidin inhibits inflammatory response induced by Aeromonas hydrophila infection and alters CD4+/CD8+ T cell ratio
Abstract
Background: Aeromonas hydrophila is an opportunistic bacterial pathogen that is associated with a number of human diseases. Hesperidin (HES) has been reported to exert antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities.
Objectives: The aim of this study was to investigate the potential effect of HES treatment on inflammatory response induced by A. hydrophila infection in murine.
Methods: A. hydrophila-infected mice were treated with HES at 250 mg/kg b.wt./week for 4 consecutive weeks. Phagocytosis, reactive oxygen species production, CD4(+)/CD8(+) T cell ratio, and CD14 expression on intestinal infiltrating monocytes were evaluated. The expression of E-selectin and intercellular adhesion molecule 1 on stimulated HUVECs and RAW macrophage was evaluated.
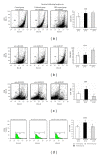
Results: Percentage of CD4(+) T cells in the intestinal tissues of infected treated mice was highly significantly increased; however, phagocytic index, ROS production, CD8(+) T cells percentage, and CD14 expression on monocytes were significantly reduced. On the other hand, HES significantly inhibited A-LPS- and A-ECP-induced E-selectin and ICAM-1 expression on HUVECs and ICAM-1 expression on RAW macrophage.
Conclusion: Present data indicated that HES has a potential role in the suppression of inflammatory response induced by A. hydrophila toxins through downmodulation of ROS production and CD14 and adhesion molecules expression, as well as increase of CD4(+)/CD8(+) cell ratio.
Figures


References
-
- Yousr AH, Napis S, Rusul GRA, Son R. Detection of aerolysin and hemolysin genes in Aeromonas spp. isolated from environmental and shellfish sources by polymerase chain reaction. ASEAN Food Journal. 2007;14(2):115–122.
-
- Nam I-Y, Joh K. Rapid detection of virulence factors of Aeromonas isolated from a trout farm by hexaplex-PCR. Journal of Microbiology. 2007;45(4):297–304. - PubMed
-
- van der Goot FG, Pattus F, Parker M, Buckley JT. The cytolytic toxin aerolysin: from the soluble form to the transmembrane channel. Toxicology. 1994;87(1–3):19–28. - PubMed
-
- Bücker R, Krug SM, Rosenthal R, et al. Aerolysin from Aeromonas hydrophila perturbs tight junction integrity and cell lesion repair in intestinal epithelial HT-29/B6 cells. Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2011;204(8):1283–1292. - PubMed
-
- Vuong C, Kocianova S, Voyich JM, et al. A crucial role for exopolysaccharide modification in bacterial biofilm formation, immune evasion, and virulence. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2004;279(52):54881–54886. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

