Thrombin based gelatin matrix and fibrin sealant mediated clot formation in the presence of clopidogrel
- PMID: 24891841
- PMCID: PMC4041347
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-9560-12-10
Thrombin based gelatin matrix and fibrin sealant mediated clot formation in the presence of clopidogrel
Abstract
Background: Platelet inhibitors are commonly used to reduce the risk of atherothrombotic events. The aim of this study was to determine the impact of platelet inhibitors, specifically clopidogrel and aspirin, on clot kinetics, strength, and/or structure during the use of thrombin based gelatin matrices and fibrin sealants.
Methods: Blood was collected and heparinized from donors on clopidogrel (and aspirin) and age matched control donors. Blood component analysis, whole blood platelet aggregometry, and activated clotting time (ACT) were used to monitor compliance to therapy and identify any differences between donor groups. Clot kinetics and strength were analyzed using thrombelastography (TEG). Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM) was used to analyze clot structure.
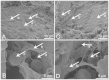
Results: Blood component profiles were similar for both donor groups. Aggregometry indicated that aggregation response to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) for clopidogrel donors was 12% of that for the controls (p = 0.0021), an expected result of clopidogrel induced platelet inhibition. However, blood from both donor groups had an elevated thrombin induced aggregation response. Heparinization of donor blood resulted in similarly elevated ACTs for both donor groups. TEG results indicated similar clot kinetics and strength between clopidogrel and control donor groups for blood alone and when clotting was induced using thrombin based gelatin matrices and fibrin sealants. FESEM images supported TEG findings in that similar morphologies were observed in ex vivo formed clots from both donor groups when thrombin based gelatin matrices and fibrin sealants were used.
Conclusion: These results suggest that platelet inhibitors do not negatively impact clot kinetics, strength, and structure when clotting is initiated with thrombin based gelatin matrices and fibrin sealants.
Keywords: Clopidogrel; Floseal; Hemostasis; Thrombelastography; Thrombin; Tisseel.
Figures







References
-
- Krumholz HM, Anderson JL, Bachelder BL, Fesmire FM, Fihn SD, Foody JM, Ho PM, Kosiborod MN, Masoudi FA, Nallamothu BK, Masoudi FA, Bonow RO, DeLong E, Estes NAM, Goff DC, Grady K, Green LA, Loth A, Peterson ED, Radford MJ, Rumsfeld JS, Shahian DM. ACC/AHA 2008 performance measures for adults with ST-elevation and non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Performance Measures (writing committee to develop performance measures for ST-elevation and non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction): developed in collaboration with the American Academy of Family Physicians and the American College of Emergency Physicians: endorsed by the American Association of Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Rehabilitation, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, and Society of Hospital Medicine. Circulation. 2008;118:2596–2648. - PubMed
-
- Adams RJ, Albers G, Alberts MJ, Benavente O, Furie K, Goldstein LB, Gorelick P, Halperin J, Harbaugh R, Johnston SC, Katzan I, Kelly-Hayes M, Kenton EJ, Marks M, Sacco RL, Schwamm LH. Update to the AHA/ASA recommendations for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack. Stroke. 2008;39:1647–1652. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.189063. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Faxon DP. Use of antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants for cardiovascular disease: current standards and best practices. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2005;6(Suppl 4):S3–S14. - PubMed
-
- Gachet C, Stierle A, Cazenave JP, Ohlmann P, Lanza F, Bouloux C, Maffrand JP. The thienopyridine PCR 4099 selectively inhibits ADP-induced platelet aggregation and fibrinogen binding without modifying the membrane glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex in rat and in man. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990;40:229–238. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90683-C. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

