Slip Reduction Rate between Minimal Invasive and Conventional Unilateral Transforaminal Interbody Fusion in Patients with Low-Grade Isthmic Spondylolisthesis
- PMID: 24891854
- PMCID: PMC4040640
- DOI: 10.14245/kjs.2013.10.4.232
Slip Reduction Rate between Minimal Invasive and Conventional Unilateral Transforaminal Interbody Fusion in Patients with Low-Grade Isthmic Spondylolisthesis
Abstract
Objective: To compare the slip reduction rate and clinical outcomes between unilateral conventional transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (conventional TLIF) and unilateral minimal invasive TLIF (minimal TLIF) with pedicle screw fixation for treatment of one level low-grade symptomatic isthmic spondylolisthesis.
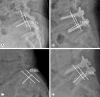
Methods: Between February 2008 and April 2012, 25 patients with low-grade isthmic spondylolisthesis underwent conventional TLIF (12 patients) and minimal TLIF (13 patients) in single university hospital by a single surgeon. Lateral radiographs of lumbar spine were taken 12 months after surgery to analyze the degree of slip reduction and the clinical outcome. All measurements were performed by a single observer.
Results: The demographic data between conventional TLIF and minimal TLIF were not different. Slip percentage was reduced from 15.00% to 8.33% in conventional TLIF, and from 14.15% to 9.62% in minimal TLIF. In both groups, slip percentage was significantly improved postoperatively (p=0.002), but no significant intergroup differences of slip percentage in preoperative and postoperative were found. The reduction rate also not different between conventional TLIF (45.41±28.80%) and minimal TLIF (32.91±32.12%, p=0.318).
Conclusion: Conventional TLIF and minimal TLIF with pedicle screw fixation showed good slip reduction in patients with one level low-grade symptomatic isthmic spondylolisthesis. The slip percentage and reduction rate were similar in the conventional TLIF and minimal TLIF.
Keywords: Conventional; Minimal invasive; Reduction rate; Slip percentage; Transforamenal lumbar interbody fusion.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Spontaneous slip reduction of low-grade isthmic spondylolisthesis following circumferential release via bilateral minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: technical note and short-term outcome.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011 Feb 15;36(4):283-9. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181cf7640. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011. PMID: 20714277
-
[Treatment of grade I and II degree degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with minimally invasive surgery-transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion under Quadrant channel].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2019 Mar 25;32(3):199-206. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0034.2019.03.002. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2019. PMID: 30921999 Chinese.
-
Comparison of O-arm navigation and microscope-assisted minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion and conventional transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for the treatment of lumbar isthmic spondylolisthesis.J Orthop Translat. 2019 Oct 31;20:107-112. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2019.10.001. eCollection 2020 Jan. J Orthop Translat. 2019. PMID: 31908941 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of clinical outcomes in surgical treatment of adult isthmic spondylolisthesis.Spine J. 2018 Aug;18(8):1441-1454. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2018.04.022. Epub 2018 May 7. Spine J. 2018. PMID: 29746966
-
Minimally Invasive Versus Traditional Open Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion for the Treatment of Single-Level Spondylolisthesis Grades 1 and 2: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.World Neurosurg. 2019 Feb;122:180-189. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2018.10.202. Epub 2018 Nov 7. World Neurosurg. 2019. PMID: 30414524
Cited by
-
Clinical, radiological and functional results of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in degenerative spondylolisthesis.N Am Spine Soc J. 2020 Jun 13;2:100011. doi: 10.1016/j.xnsj.2020.100011. eCollection 2020 Aug. N Am Spine Soc J. 2020. PMID: 35141582 Free PMC article.
-
Enlargement of Neural Foramina and Dynamic Stabilization in Spondylolisthesis without Restoring the Alignment: Technical Note.Korean J Spine. 2016 Mar;13(1):37-9. doi: 10.14245/kjs.2016.13.1.37. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Korean J Spine. 2016. PMID: 27123030 Free PMC article.
-
Traumatic Vertebral Fracture in a Patient With Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Rare Complication.Cureus. 2021 Oct 24;13(10):e19004. doi: 10.7759/cureus.19004. eCollection 2021 Oct. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34853743 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and Radiological Comparison of Semirigid (WavefleX) and Rigid System for the Lumbar Spine.Korean J Spine. 2016 Jun;13(2):57-62. doi: 10.14245/kjs.2016.13.2.57. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Korean J Spine. 2016. PMID: 27437014 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barbagallo GM, Certo F, Sciacca G, Albanese V. Bilateral tubular minimally invasive approach for decompression, reduction and fixation in lumbosacral lythicspondylolisthesis. Neurosurg Focus. 2013;35:Video 9. - PubMed
-
- Dhall SS, Wang MY, Mummaneni PV. Clinical and radiographic comparison of mini-open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in 42 patients with long-term follow-up. J Neurosurg Spine. 2008;9:560–565. - PubMed
-
- Foley KT, Holly LT, Schwender JD. Minimally invasive lumbar fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2003;28:S26–S35. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous