Design of glucagon-like Peptide-1 receptor agonist for diabetes mellitus from traditional chinese medicine
- PMID: 24891870
- PMCID: PMC4033432
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/385120
Design of glucagon-like Peptide-1 receptor agonist for diabetes mellitus from traditional chinese medicine
Abstract
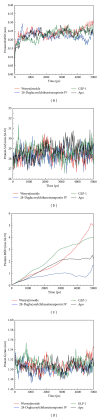
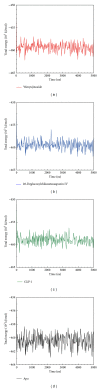
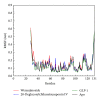
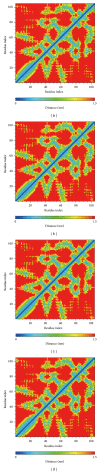
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is a promising target for diabetes mellitus (DM) therapy and reduces the occurrence of diabetes due to obesity. However, GLP-1 will be hydrolyzed soon by the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4). We tried to design small molecular drugs for GLP-1 receptor agonist from the world's largest traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) Database@Taiwan. According to docking results of virtual screening, we selected 2 TCM compounds, wenyujinoside and 28-deglucosylchikusetsusaponin IV, for further molecular dynamics (MD) simulation. GLP-1 was assigned as the control compound. Based on the results of root mean square deviation (RMSD), solvent accessible surface (SAS), mean square deviation (MSD), Gyrate, total energy, root mean square fluctuation (RMSF), matrices of smallest distance of residues, database of secondary structure assignment (DSSP), cluster analysis, and distance of H-bond, we concluded that all the 3 compounds could bind and activate GLP-1 receptor by computational simulation. Wenyujinoside and 28-deglucosylchikusetsusaponin IV were the TCM compounds that could be GLP-1 receptor agonists.
Figures








References
-
- Finan B, Ma T, Ottaway N, et al. Unimolecular dual incretins maximize metabolic benefits in rodents, monkeys, and humans. Science Translational Medicine. 2013;5(209)209ra151 - PubMed
-
- Randle PJ, Garland PB, Hales CN, Newsholme EA. The glucose fatty-acid cycle. Its role in insulin sensitivity and the metabolic disturbances of diabetes mellitus. The Lancet. 1963;281(7285):785–789. - PubMed
-
- Sun HY, Ke FD, Wen JS. Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2010;362(25):2425–2426. - PubMed
-
- Nerup J, Platz P, Ortved Andersen O. HL A antigens and diabetes mellitus. The Lancet. 1974;2(7885):864–866. - PubMed
-
- Bottazzo GF, Florin Christensen A, Doniach D. Islet cell antibodies in diabetes mellitus with autoimmune polyendocrine deficiencies. The Lancet. 1974;2(7892):1279–1283. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

