Protein-protein interactions and genetic diseases: The interactome
- PMID: 24892209
- PMCID: PMC4165798
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.05.028
Protein-protein interactions and genetic diseases: The interactome
Abstract
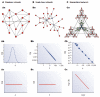
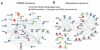
Protein-protein interactions mediate essentially all biological processes. Despite the quality of these data being widely questioned a decade ago, the reproducibility of large-scale protein interaction data is now much improved and there is little question that the latest screens are of high quality. Moreover, common data standards and coordinated curation practices between the databases that collect the interactions have made these valuable data available to a wide group of researchers. Here, I will review how protein-protein interactions are measured, collected and quality controlled. I discuss how the architecture of molecular protein networks has informed disease biology, and how these data are now being computationally integrated with the newest genomic technologies, in particular genome-wide association studies and exome-sequencing projects, to improve our understanding of molecular processes perturbed by genetics in human diseases. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled: From Genome to Function.
Keywords: Complex human disease; Genetics and proteomics; Protein–protein interaction.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

