Lung tumor motion change during stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT): an evaluation using MRI
- PMID: 24892328
- PMCID: PMC5711053
- DOI: 10.1120/jacmp.v15i3.4434
Lung tumor motion change during stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT): an evaluation using MRI
Abstract
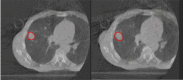
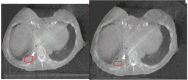
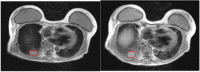
The purpose of this study is to investigate changes in lung tumor internal target volume during stereotactic body radiotherapy treatment (SBRT) using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Ten lung cancer patients (13 tumors) undergoing SBRT (48 Gy over four consecutive days) were evaluated. Each patient underwent three lung MRI evaluations: before SBRT (MRI-1), after fraction 3 of SBRT (MRI-3), and three months after completion of SBRT (MRI-3m). Each MRI consisted of T1-weighted images in axial plane through the entire lung. A cone-beam CT (CBCT) was taken before each fraction. On MRI and CBCT taken before fractions 1 and 3, gross tumor volume (GTV) was contoured and differences between the two volumes were compared. Median tumor size on CBCT before fractions1 (CBCT-1) and 3 (CBCT-3) was 8.68 and 11.10 cm3, respectively. In 12 tumors, the GTV was larger on CBCT-3 compared to CBCT-1 (median enlargement, 1.56 cm3). Median tumor size on MRI-1, MRI-3, and MRI-3m was 7.91, 11.60, and 3.33 cm3, respectively. In all patients, the GTV was larger on MRI-3 compared to MRI-1 (median enlargement, 1.54 cm3). In all patients, GTV was smaller on MRI-3m compared to MRI-1 (median shrinkage, 5.44 cm3). On CBCT and MRI, all patients showed enlargement of the GTV during the treatment week of SBRT, except for one patient who showed minimal shrinkage (0.86 cm3). Changes in tumor volume are unpredictable; therefore, motion and breathing must be taken into account during treatment planning, and image-guided methods should be used, when treating with large fraction sizes.
Figures
References
-
- Timmerman RD, Kavanagh BD, Cho LC, Papiez L, Xing L. Stereotactic body radiation therapy in multiple organ sites. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(8):947–52. - PubMed
-
- Zhang J, Yang F, Li B, et al. Which is the optimal biologically effective dose of stereotactic body radiotherapy for Stage I non‐small‐cell lung cancer? A meta‐analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;81(4):e305–e316. - PubMed
-
- Yeung AR, Li JG, Shi W, et al. Tumor localization using cone‐beam CT reduces setup margins in conventionally fractionated radiotherapy for lung tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009;74(4):1100–07. - PubMed
-
- Seppenwoolde Y, Shirato H, Kitamura K, et al. Precise and real‐time measurement of 3D tumor motion in lung due to breathing and heartbeat, measured during radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002;53(4):822–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

