Interplay effect of angular dependence and calibration field size of MapCHECK 2 on RapidArc quality assurance
- PMID: 24892335
- PMCID: PMC5711069
- DOI: 10.1120/jacmp.v15i3.4638
Interplay effect of angular dependence and calibration field size of MapCHECK 2 on RapidArc quality assurance
Abstract
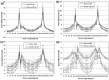
The purpose of this study is to investigate an effect of angular dependence and calibration field size of MapCHECK 2 on RapidArc QA for 6, 8, 10, and 15 MV. The angular dependence was investigated by comparing MapCHECK 2 measurements in MapPHAN-MC2 to the corresponding Eclipse calculations every 10° using 10× 10 cm2 and 3 × 3 cm2 fields. Fourteen patients were selected to make RapidArc plans using the four energies, and verification plans were delivered to two phantom setups: MapCHECK 2/MapPHAN phantom (MapPHAN QA) and MapCHECK 2 on an isocentric mounting fixture (IMF QA). Migration of MapCHECK 2 on IMF was simulated by splitting arcs every 10° and displacing an isocenter of each partial arc in the Eclipse system (IMFACTUAL QA). To investigate the effect of calibration field size, MapCHECK 2 was calibrated by two field sizes (10 × 10 cm2 and 3 × 3 cm2) and applied to all QA measurements. The γ test was implemented using criteria of 1%/1 mm, 2%/2 mm, and 3%/3 mm. A mean dose of all compared points for each plan was compared with respect to a mean effective field size of the RapidArc plan. The angular dependence was considerably high at gantry angles of 90° ± 10° and 270° ± 10° (for 10 × 10/3 × 3 cm2 at 90°, 30.6% ± 6.6%/33.4%± 5.8% (6 MV), 17.3% ± 5.3%/15.0% ± 6.8% (8 MV), 8.9%± 2.9%/7.8% ± 3.2% (10 MV), and 2.2% ± 2.3%/-1.3% ± 2.6% (15 MV)). For 6 MV, the angular dependence significantly deteriorated the γ passing rate for plans of large field size in MapPHAN QA (< 90% using 3%/3 mm); however, these plans passed the γ test in IMFACTUAL QA (> 95%). The different calibration field sizes did not make any significant dose difference for both MapPHAN QA and IMFACTUAL QA. For 8, 10, and 15 MV, the angular dependence does not make any clinically meaningful impact on MapPHAN QA. Both MapPHAN QA and IMFACTUAL QA presented clinically acceptable γ passing rates using 3%/3 mm. MapPHAN QA showed better passing rates than IMFACTUAL QA for the tighter criteria. The 10 × 10 cm2 calibration showed better agreement for plans of small effective field size (< 5 × 5 cm2) in MapPHAN QA. There was no statistical difference between IMF QA and IMFACTUAL QA. In conclusion, MapPHAN QA is not recommended for plans of large field size, especially for 6 MV, and MapCHECK2 should be calibrated using a field size similar to a mean effective field size of a RapidArc plan for better agreement for IMF QA.
Figures





References
-
- Guckenberger M, Richter A, Krieger T, Wilbert J, Baier K, Flentje M. Is a single arc sufficient in volumetric‐modulated arc therapy (VMAT) for complex‐shaped target volumes? Radiother Oncol. 2009;93(2):259–65. - PubMed
-
- Clivio A, Fogliata A, Franzetti‐Pellanda A, et al. Volumetric‐modulated arc radiotherapy for carcinomas of the anal canal: a treatment planning comparison with fixed field IMRT. Radiother Oncol. 2009;92(1):118–24. - PubMed
-
- Davidson MT, Blake SJ, Batchelar DL, Cheung P, Mah K. Assessing the role of volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) relative to IMRT and helical tomotherapy in the management of localized, locally advanced, and postoperative prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;80(5):1550–558. - PubMed
-
- Matuszak MM, Yan D, Grills I, Martinez A. Clinical applications of volumetric modulated arc therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;77(2):608–16. - PubMed
-
- Lu S, Cheng JC, Kuo S, et al. Volumetric modulated arc therapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a dosimetric comparison with TomoTherapy and step‐and‐shoot IMRT Radiother Oncol. 2012;104(3):324–30. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

