Optimization strategies for pulsed low-dose-rate IMRT of recurrent lung and head and neck cancers
- PMID: 24892337
- PMCID: PMC5711051
- DOI: 10.1120/jacmp.v15i3.4661
Optimization strategies for pulsed low-dose-rate IMRT of recurrent lung and head and neck cancers
Abstract
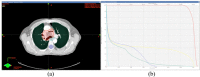
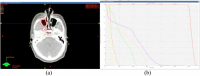
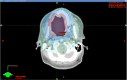
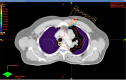
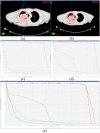
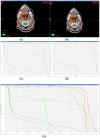
Pulsed low-dose-rate radiotherapy (PLDR) has been proven to be a valid method of reirradiation. Previous studies of recurrent cancer radiotherapy were mainly based on conventional 3D CRT and VMAT delivery techniques. There are difficulties in IMRT planning using existing commercial treatment planning systems (TPS) to meet the PLDR protocol. This work focuses on PLDR using ten-field IMRT and a commercial TPS for two specific sites: recurrent lung cancers and head and neck cancers. Our PLDR protocol requires that the maximum dose to the PTV be less than 0.4 Gy and the mean dose to be 0.2 Gy per field. We investigated various planning strategies to meet the PLDR requirements for 20 lung and head and neck patients. The PTV volume for lung cases ranged from 101.7 to 919.4 cm3 and the maximum dose to the PTV ranged from 0.22 to 0.39 Gy. The PTV volume for head and neck cases ranged from 66.2 to 282.1 cm3 and the maximum dose to the PTV ranged from 0.21 to 0.39 Gy. With special beam arrangements and dosimetry parameters, it is feasible to use a commercial TPS to generate quality PLDR IMRT plans for lung and head and neck reirradiation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intensity-modulated radiation therapy for pancreatic and prostate cancer using pulsed low-dose rate delivery techniques.Med Dosim. 2014 Winter;39(4):330-6. doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2014.05.008. Epub 2014 Jul 30. Med Dosim. 2014. PMID: 25087084 Clinical Trial.
-
Investigation of pulsed IMRT and VMAT for re-irradiation treatments: dosimetric and delivery feasibilities.Phys Med Biol. 2013 Nov 21;58(22):8179-96. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/58/22/8179. Phys Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 24200917
-
A dosimetric comparison of the use of equally spaced beam (ESB), beam angle optimization (BAO), and volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) in head and neck cancers treated by intensity modulated radiotherapy.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2019 Nov;20(11):121-130. doi: 10.1002/acm2.12748. Epub 2019 Oct 8. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2019. PMID: 31593367 Free PMC article.
-
Pulsed low dose-rate radiotherapy: radiobiology and dosimetry.Phys Med Biol. 2022 Jan 28;67(3). doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ac4c2f. Phys Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 35038688 Review.
-
Reirradiation of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas: a pragmatic approach, part II: radiation technique and fractionations.Radiol Med. 2023 Aug;128(8):1007-1021. doi: 10.1007/s11547-023-01671-0. Epub 2023 Jul 6. Radiol Med. 2023. PMID: 37415056 Review.
Cited by
-
Local Control and Toxicity of External Beam Reirradiation With a Pulsed Low-dose-rate Technique.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2018 Mar 15;100(4):959-964. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.12.012. Epub 2017 Dec 23. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2018. PMID: 29485075 Free PMC article.
-
Pulsed low-dose rate radiotherapy for recurrent bone sarcomas: case reports and brief review.Radiat Oncol J. 2024 Mar;42(1):88-94. doi: 10.3857/roj.2023.00815. Epub 2024 Feb 13. Radiat Oncol J. 2024. PMID: 38549388 Free PMC article.
-
Local Tumor Control and Normal Tissue Toxicity of Pulsed Low-Dose Rate Radiotherapy for Recurrent Lung Cancer: An In Vivo Animal Study.Dose Response. 2015 May 25;13(2):1559325815588507. doi: 10.1177/1559325815588507. eCollection 2015 Apr-Jun. Dose Response. 2015. PMID: 26675811 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hall EJ and Brenner DJ. The dose‐rate effect revisited: radiobiological considerations of importance in radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1991;21(6):1403–14. - PubMed
-
- Steel GG, Deacon JM, Duchesne GM, Horwich A, Keiland LR, Peacock JH. The dose‐rate effect in human tumour cells. Radiother Oncol. 1987;9(4):299–310. - PubMed
-
- Ma CM, Luxton G, Orton CG. Point/Counterpoint: Pulsed reduced dose rate radiation therapy is likely to become the treatment modality of choice for recurrent cancers. Med Phys. 2011;38(9):4909–11. - PubMed
-
- Cannon GM, Tome WA, Robins HI, Howard SP. Pulsed reduced dose‐rate radiotherapy: case report, a novel retreatment strategy in the management of recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. J Neurooncol. 2007;83(3):307–11. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

