Extracellular vesicle-mediated transfer of genetic information between the hematopoietic system and the brain in response to inflammation
- PMID: 24893313
- PMCID: PMC4043485
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001874
Extracellular vesicle-mediated transfer of genetic information between the hematopoietic system and the brain in response to inflammation
Erratum in
-
Correction: Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Transfer of Genetic Information between the Hematopoietic System and the Brain in Response to Inflammation.PLoS Biol. 2018 Mar 12;16(3):e1002623. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002623. eCollection 2018 Mar. PLoS Biol. 2018. PMID: 29529027 Free PMC article.
Abstract
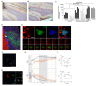
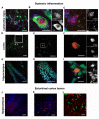
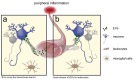
Mechanisms behind how the immune system signals to the brain in response to systemic inflammation are not fully understood. Transgenic mice expressing Cre recombinase specifically in the hematopoietic lineage in a Cre reporter background display recombination and marker gene expression in Purkinje neurons. Here we show that reportergene expression in neurons is caused by intercellular transfer of functional Cre recombinase messenger RNA from immune cells into neurons in the absence of cell fusion. In vitro purified secreted extracellular vesicles (EVs) from blood cells contain Cre mRNA, which induces recombination in neurons when injected into the brain. Although Cre-mediated recombination events in the brain occur very rarely in healthy animals, their number increases considerably in different injury models, particularly under inflammatory conditions, and extend beyond Purkinje neurons to other neuronal populations in cortex, hippocampus, and substantia nigra. Recombined Purkinje neurons differ in their miRNA profile from their nonrecombined counterparts, indicating physiological significance. These observations reveal the existence of a previously unrecognized mechanism to communicate RNA-based signals between the hematopoietic system and various organs, including the brain, in response to inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
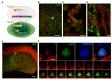
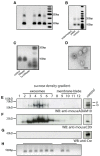
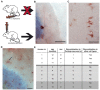
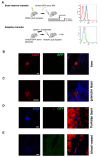

Comment in
-
Inflammation triggers RNA transfer from blood cells to brain neurons.PLoS Biol. 2014 Jun 3;12(6):e1001875. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001875. eCollection 2014 Jun. PLoS Biol. 2014. PMID: 24892283 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Signalling: vesicle vehicles of genetic information.Nat Rev Genet. 2014 Aug;15(8):514. doi: 10.1038/nrg3780. Epub 2014 Jun 24. Nat Rev Genet. 2014. PMID: 24958437 No abstract available.
-
A previously unrecognized mechanism for communication between the hematopoietic system and the brain.Neurosurgery. 2014 Oct;75(4):N22-3. doi: 10.1227/01.neu.0000454763.29872.6b. Neurosurgery. 2014. PMID: 25232792 No abstract available.
References
-
- Terada N, Hamazaki T, Oka M, Hoki M, Mastalerz DM, et al. (2002) Bone marrow cells adopt the phenotype of other cells by spontaneous cell fusion. Nature 416: 542–545. - PubMed
-
- Ying QL, Nichols J, Evans EP, Smith AG (2002) Changing potency by spontaneous fusion. Nature 416: 545–548. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Dolado M, Pardal R, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Fike JR, Lee HO, et al. (2003) Fusion of bone-marrow-derived cells with Purkinje neurons, cardiomyocytes and hepatocytes. Nature 425: 968–973. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

