Combined effect of sesamin and soybean phospholipid on hepatic fatty acid metabolism in rats
- PMID: 24894022
- PMCID: PMC4042142
- DOI: 10.3164/jcbn.13-83
Combined effect of sesamin and soybean phospholipid on hepatic fatty acid metabolism in rats
Abstract
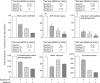
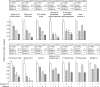
We studied the combined effect of sesamin (1:1 mixture of sesamin and episesamine) and soybean phospholipid on lipid metabolism in rats. Male rats were fed diets supplemented with 0 or 2 g/kg sesamin, and containing 0 or 50 g/kg soybean phospholipid, for 19 days. Sesamin and soybean phospholipid decreased serum triacylglycerol concentrations and the combination of these compounds further decreased the parameter in an additive fashion. Soybean phospholipid but not sesamin reduced the hepatic concentration of triacylglycerol. The combination failed to cause a strong decrease in hepatic triacylglycerol concentration, presumably due to the up-regulation of Cd36 by sesamin. Combination of sesamin and soybean phospholipid decreased the activity and mRNA levels of hepatic lipogenic enzymes in an additive fashion. Sesamin strongly increased the parameters of hepatic fatty acid oxidation enzymes. Soybean phospholipid increased hepatic activity of 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase although it failed to affect the activity of other enzymes involved in fatty acid oxidation. Sesamin strongly increased hepatic concentration of carnitine. Sesamin and soybean phospholipid combination further increased this parameter, accompanying a parallel increase in mRNA expression of carnitine transporter. These changes can account for the strong decrease in serum triacylglycerol in rats fed a diet containing both sesamin and soybean phospholipid.
Keywords: carnitine; hepatic fatty acid oxidation; hepatic lipogenesis; sesamin; soybean phospholipid.
Figures

References
-
- Fukuda Y, Nagata M, Osawa T, Namiki M. Contribution of lignan analogues to antioxidative activity of refined unroasted sesame seed oil. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1986;63:1027–1031.
-
- Ashakumary L, Rouyer IA, Takahashi Y, et al. Sesamin, a sesame lignan, is a potent inducer of hepatic fatty acid oxidation in the rat. Metabolism. 1999;48:1303–1313. - PubMed
-
- Ide T, Ashakumary L, Takahashi Y, Kushiro M, Fukuda N, Sugano M. Sesamin, a sesame lignan, decreases fatty acid synthesis in rat liver accompanying the down-regulation of sterol regulatory element binding protein-1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001;1534:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Hirata F, Fujita K, Ishikura Y, Hosoda K, Ishikawa T, Nakamura H. Hypocholesterolemic effect of sesame lignan in humans. Atherosclerosis. 1996;122:135–136. - PubMed
-
- Kushiro M, Masaoka T, Hageshita S, Takahashi Y, Ide T, Sugano M. Comparative effect of sesamin and episesamin on the activity and gene expression of enzymes in fatty acid oxidation and synthesis in rat liver. J Nutr Biochem. 2002;13:289–295. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

