Tumor targeting RGD conjugated bio-reducible polymer for VEGF siRNA expressing plasmid delivery
- PMID: 24894645
- PMCID: PMC4090046
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.05.021
Tumor targeting RGD conjugated bio-reducible polymer for VEGF siRNA expressing plasmid delivery
Abstract
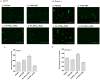
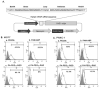
Targeted delivery of therapeutic genes to the tumor site is critical for successful and safe cancer gene therapy. The arginine grafted bio-reducible poly (cystamine bisacrylamide-diaminohexane, CBA-DAH) polymer (ABP) conjugated poly (amido amine) (PAMAM), PAM-ABP (PA) was designed previously as an efficient gene delivery carrier. To achieve high efficacy in cancer selective delivery, we developed the tumor targeting bio-reducible polymer, PA-PEG1k-RGD, by conjugating cyclic RGDfC (RGD) peptides, which bind αvβ3/5 integrins, to the PAM-ABP using polyethylene glycol (PEG, 1 kDa) as a spacer. Physical characterization showed nanocomplex formation with bio-reducible properties between PA-PEG1k-RGD and plasmid DNA (pDNA). In transfection assays, PA-PEG1k-RGD showed significantly higher transfection efficiency in comparison with PAM-ABP or PA-PEG1k-RAD in αvβ3/5 positive MCF7 breast cancer and PANC-1 pancreatic cancer cells. The targeting ability of PA-PEG1k-RGD was further established using a competition assay. To confirm the therapeutic effect, the VEGF siRNA expressing plasmid was constructed and then delivered into cancer cells using PA-PEG1k-RGD. PA-PEG1k-RGD showed 20-59% higher cellular uptake rate into MCF7 and PANC-1 than that of non-targeted polymers. In addition, MCF7 and PANC-1 cancer cells transfected with PA-PEG1k-RGD/pshVEGF complexes had significantly decreased VEGF gene expression (51-71%) and cancer cell viability (35-43%) compared with control. These results demonstrate that a tumor targeting bio-reducible polymer with an anti-angiogenic therapeutic gene could be used for efficient and safe cancer gene therapy.
Keywords: Bio-reducible polymer; Cancer gene therapy; RGD peptides; Targeted gene delivery; VEGF siRNA.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



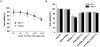
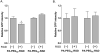


Similar articles
-
Design of PEI-conjugated bio-reducible polymer for efficient gene delivery.Int J Pharm. 2018 Jul 10;545(1-2):295-305. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.04.051. Epub 2018 Apr 23. Int J Pharm. 2018. PMID: 29698820 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of dendrimer type bio-reducible polymer as a siRNA delivery carrier for cancer therapy.J Control Release. 2015 Jul 10;209:179-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.04.039. Epub 2015 Apr 30. J Control Release. 2015. PMID: 25937533 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoma targeting peptide conjugated bio-reducible polymer complexed with oncolytic adenovirus for cancer gene therapy.J Control Release. 2015 Dec 28;220(Pt B):691-703. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.09.068. Epub 2015 Oct 3. J Control Release. 2015. PMID: 26437261 Free PMC article.
-
RGD-based strategies for selective delivery of therapeutics and imaging agents to the tumour vasculature.Drug Resist Updat. 2005 Dec;8(6):381-402. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2005.10.002. Epub 2005 Nov 23. Drug Resist Updat. 2005. PMID: 16309948 Review.
-
Conjugated Polymers for Gene Delivery and Photothermal Gene Expression.Chempluschem. 2022 May;87(5):e202200073. doi: 10.1002/cplu.202200073. Chempluschem. 2022. PMID: 35589625 Review.
Cited by
-
A Tumor-specific MicroRNA Recognition System Facilitates the Accurate Targeting to Tumor Cells by Magnetic Nanoparticles.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2016 May 3;5(5):e318. doi: 10.1038/mtna.2016.28. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2016. PMID: 27138178 Free PMC article.
-
Development of iRGD-Modified Peptide Carriers for Suicide Gene Therapy of Uterine Leiomyoma.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Feb 2;13(2):202. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13020202. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 33540912 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-Clinical and Clinical Applications of Small Interfering RNAs (siRNA) and Co-Delivery Systems for Pancreatic Cancer Therapy.Cells. 2021 Nov 29;10(12):3348. doi: 10.3390/cells10123348. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34943856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced tumor targeting of cRGD peptide-conjugated albumin nanoparticles in the BxPC-3 cell line.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 12;6:31539. doi: 10.1038/srep31539. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27515795 Free PMC article.
-
PAMAM-cRGD mediating efficient siRNA delivery to spermatogonial stem cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Dec 18;10(1):399. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1506-4. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31852526 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu F, Huang L. Development of non-viral vectors for systemic gene delivery. J Control Release. 2002;78:259–66. - PubMed
-
- Wong SY, Pelet JM, Putnam D. Polymer systems for gene delivery—past, present, and future. Prog Polym Sci. 2007;32:799–837.
-
- Fischer D, Li Y, Ahlemeyer B, Krieglstein J, Kissel T. In vitro cytotoxicity testing of polycations: influence of polymer structure on cell viability and hemolysis. Biomaterials. 2003;24:1121–31. - PubMed
-
- Mintzer MA, Simanek EE. Nonviral vectors for gene delivery. Chem rev. 2008;109:259–302. - PubMed
-
- Lim YB, Kim SM, Suh H, Park JS. Biodegradable, endosome disruptive, and cationic network-type polymer as a highly efficient and nontoxic gene delivery carrier. Bioconjugate Chem. 2002;13:952–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

