ALK-negative anaplastic large cell lymphoma is a genetically heterogeneous disease with widely disparate clinical outcomes
- PMID: 24894770
- PMCID: PMC4148769
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2014-04-571091
ALK-negative anaplastic large cell lymphoma is a genetically heterogeneous disease with widely disparate clinical outcomes
Abstract
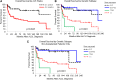
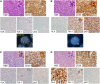
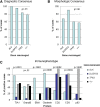
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-negative anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) is a CD30-positive T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma that morphologically resembles ALK-positive ALCL but lacks chromosomal rearrangements of the ALK gene. The genetic and clinical heterogeneity of ALK-negative ALCL has not been delineated. We performed immunohistochemistry and fluorescence in situ hybridization on 73 ALK-negative ALCLs and 32 ALK-positive ALCLs and evaluated the associations among pathology, genetics, and clinical outcome. Chromosomal rearrangements of DUSP22 and TP63 were identified in 30% and 8% of ALK-negative ALCLs, respectively. These rearrangements were mutually exclusive and were absent in ALK-positive ALCLs. Five-year overall survival rates were 85% for ALK-positive ALCLs, 90% for DUSP22-rearranged ALCLs, 17% for TP63-rearranged ALCLs, and 42% for cases lacking all 3 genetic markers (P < .0001). Hazard ratios for death in these 4 groups after adjusting for International Prognostic Index and age were 1.0 (reference group), 0.58, 8.63, and 4.16, respectively (P = 7.10 × 10(-5)). These results were similar when restricted to patients receiving anthracycline-based chemotherapy, as well as to patients not receiving stem cell transplantation. Thus, ALK-negative ALCL is a genetically heterogeneous disease with widely disparate outcomes following standard therapy. DUSP22 and TP63 rearrangements may serve as predictive biomarkers to help guide patient management.
Figures
Comment in
-
What is a true ALCL?Blood. 2014 Aug 28;124(9):1385-6. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-06-581694. Blood. 2014. PMID: 25170112 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Delsol G, Falini B, Muller-Hermelink HK, et al. Anaplastic large cell lymphoma, ALK-positive. In: Swerdlow S, Campo E, Harris N, et al., editors. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2008:312-316.
-
- Mason DY, Harris NL, Delsol G, et al. Anaplastic large cell lymphoma, ALK-negative. In: Swerdlow S, Campo E, Harris N, et al., editors. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2008:317-319.
-
- Gascoyne RD, Aoun P, Wu D, et al. Prognostic significance of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) protein expression in adults with anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Blood. 1999;93(11):3913–3921. - PubMed
-
- Falini B, Pileri S, Zinzani PL, et al. ALK+ lymphoma: clinico-pathological findings and outcome. Blood. 1999;93(8):2697–2706. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

