BMP signaling balances murine myeloid potential through SMAD-independent p38MAPK and NOTCH pathways
- PMID: 24894772
- PMCID: PMC4102711
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2014-02-556993
BMP signaling balances murine myeloid potential through SMAD-independent p38MAPK and NOTCH pathways
Abstract
Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling regulates early hematopoietic development, proceeding from mesoderm patterning through the progressive commitment and differentiation of progenitor cells. The BMP pathway signals largely through receptor-mediated activation of Mothers Against Decapentaplegic homolog (SMAD) proteins, although alternate pathways are modulated through various components of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling. Using a conditional, short hairpin RNA (shRNA)-based knockdown system in the context of differentiating embryonic stem cells (ESCs), we demonstrated previously that Smad1 promotes hemangioblast specification, but then subsequently restricts primitive progenitor potential. Here we show that co-knockdown of Smad5 restores normal progenitor potential of Smad1-depleted cells, suggesting opposing functions for Smad1 and Smad5. This balance was confirmed by cotargeting Smad1/5 with a specific chemical antagonist, LDN193189 (LDN). However, we discovered that LDN treatment after hemangioblast commitment enhanced primitive myeloid potential. Moreover, inhibition with LDN (but not SMAD depletion) increased expression of Delta-like ligands Dll1 and Dll3 and NOTCH activity; abrogation of NOTCH activity restored LDN-enhanced myeloid potential back to normal, corresponding with expression levels of the myeloid master regulator, C/EBPα. LDN but not SMAD activity was also associated with activation of the p38MAPK pathway, and blocking this pathway was sufficient to enhance myelopoiesis. Therefore, NOTCH and p38MAPK pathways balance primitive myeloid progenitor output downstream of the BMP pathway.
© 2014 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures

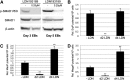
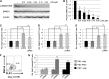


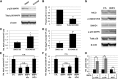

Similar articles
-
Transcriptional factors smad1 and smad9 act redundantly to mediate zebrafish ventral specification downstream of smad5.J Biol Chem. 2014 Mar 7;289(10):6604-6618. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.549758. Epub 2014 Jan 31. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24488494 Free PMC article.
-
Dorsomorphin and LDN-193189 inhibit BMP-mediated Smad, p38 and Akt signalling in C2C12 cells.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010 Nov;42(11):1802-7. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2010.07.018. Epub 2010 Aug 5. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20691279 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide mapping of SMAD target genes reveals the role of BMP signaling in embryonic stem cell fate determination.Genome Res. 2010 Jan;20(1):36-44. doi: 10.1101/gr.092114.109. Epub 2009 Nov 19. Genome Res. 2010. PMID: 19926752 Free PMC article.
-
BMP-Smad 1/5/8 signalling in the development of the nervous system.Prog Neurobiol. 2013 Oct;109:28-41. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.07.002. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Prog Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23891815 Review.
-
Blockade of Jagged/Notch pathway abrogates transforming growth factor β2-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human retinal pigment epithelium cells.Curr Mol Med. 2014 May;14(4):523-34. doi: 10.2174/1566524014666140331230411. Curr Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24694299 Review.
Cited by
-
Loss of Myeloid BMPR1a Alters Differentiation and Reduces Mouse Prostate Cancer Growth.Front Oncol. 2020 Apr 7;10:357. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00357. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32318332 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling murine yolk sac hematopoiesis with embryonic stem cell culture systems.Front Biol (Beijing). 2014 Oct;9(5):339-346. doi: 10.1007/s11515-014-1328-9. Front Biol (Beijing). 2014. PMID: 25558247 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in understanding contextual TGFβ signaling.F1000Res. 2017 May 26;6:749. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.11295.1. eCollection 2017. F1000Res. 2017. PMID: 28649369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elevated DLL3 in stomach cancer by tumor-associated macrophages enhances cancer-cell proliferation and cytokine secretion of macrophages.Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2021 Nov 25;10:goab052. doi: 10.1093/gastro/goab052. eCollection 2022. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2021. PMID: 35382168 Free PMC article.
-
Notch signaling mitigates chemotherapy toxicity by accelerating hematopoietic stem cells proliferation via c-Myc.Am J Transl Res. 2020 Oct 15;12(10):6723-6739. eCollection 2020. Am J Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 33194068 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen D, Zhao M, Mundy GR. Bone morphogenetic proteins. Growth Factors. 2004;22(4):233–241. - PubMed
-
- Winnier G, Blessing M, Labosky PA, Hogan BL. Bone morphogenetic protein-4 is required for mesoderm formation and patterning in the mouse. Genes Dev. 1995;9(17):2105–2116. - PubMed
-
- Zhang C, Evans T. BMP-like signals are required after the midblastula transition for blood cell development. Dev Genet. 1996;18(3):267–278. - PubMed
-
- Chang H, Huylebroeck D, Verschueren K, Guo Q, Matzuk MM, Zwijsen A. Smad5 knockout mice die at mid-gestation due to multiple embryonic and extraembryonic defects. Development. 1999;126(8):1631–1642. - PubMed
-
- Yang X, Castilla LH, Xu X, et al. Angiogenesis defects and mesenchymal apoptosis in mice lacking SMAD5. Development. 1999;126(8):1571–1580. - PubMed

