Impact of MLL5 expression on decitabine efficacy and DNA methylation in acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 24895338
- PMCID: PMC4562534
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2013.101386
Impact of MLL5 expression on decitabine efficacy and DNA methylation in acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
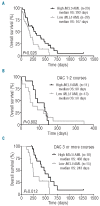
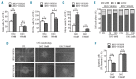
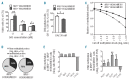
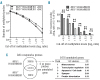
Hypomethylating agents are widely used in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes and unfit patients with acute myeloid leukemia. However, it is not well understood why only some patients respond to hypomethylating agents. We found previously that the effect of decitabine on hematopoietic stem cell viability differed between Mll5 wild-type and null cells. We, therefore, investigated the role of MLL5 expression levels on outcome of acute myeloid leukemia patients who were treated with decitabine. MLL5 above the median expression level predicted longer overall survival independent of DNMT3A mutation status in bivariate analysis (median overall survival for high vs. low MLL5 expression 292 vs. 167 days; P=0.026). In patients who received three or more courses decitabine, high MLL5 expression and wild-type DNMT3A independently predicted improved overall survival (median overall survival for high vs. low MLL5 expression 468 vs. 243 days; P=0.012). In transformed murine cells, loss of Mll5 was associated with resistance to low-dose decitabine, less global DNA methylation in promoter regions, and reduced DNA demethylation upon decitabine treatment. Together, these data support our clinical observation of improved outcome in decitabine-treated patients who express MLL5 at high levels, and suggest a mechanistic role of MLL5 in the regulation of DNA methylation.
Copyright© Ferrata Storti Foundation.
Figures
Comment in
-
MLL5 expression as a biomarker for DNA hypermethylation and sensitivity to epigenetic therapy.Haematologica. 2014 Sep;99(9):1405-7. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2014.113357. Haematologica. 2014. PMID: 25176980 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lowenberg B. Acute myeloid leukemia: the challenge of capturing disease variety. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2008;1:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Shih AH, Abdel-Wahab O, Patel JP, Levine RL. The role of mutations in epigenetic regulators in myeloid malignancies. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12(9):599–612. - PubMed
-
- Burnett A, Wetzler M, Lowenberg B. Therapeutic advances in acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(5):487–94. - PubMed
-
- Lubbert M, Suciu S, Baila L, Ruter BH, Platzbecker U, Giagounidis A, et al. Low-dose decitabine versus best supportive care in elderly patients with intermediate- or high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) ineligible for intensive chemotherapy: final results of the randomized phase III study of the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Leukemia Group and the German MDS Study Group. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(15):1987–96. - PubMed
-
- Kantarjian HM, Thomas XG, Dmoszynska A, Wierzbowska A, Mazur G, Mayer J, et al. Multicenter, randomized, open-label, phase III trial of decitabine versus patient choice, with physician advice, of either supportive care or low-dose cytarabine for the treatment of older patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(21):2670–7. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

