BRP, a polysaccharide fraction isolated from Boschniakia rossica, protects against galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide induced hepatic failure in mice
- PMID: 24895481
- PMCID: PMC4042147
- DOI: 10.3164/jcbn.13-105
BRP, a polysaccharide fraction isolated from Boschniakia rossica, protects against galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide induced hepatic failure in mice
Abstract
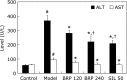
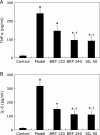
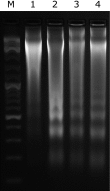
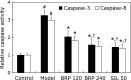
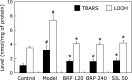
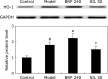
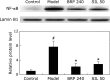
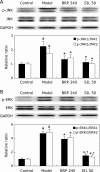
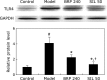
The aim of this study was to investigate the hepatoprotective effect of BRP, a polysaccharide fraction isolated from Boschniakia rossica, against galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide induced fulminant hepatic failure. Mice were injected with a single dose of galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide with or without pretreatment of BRP. Results showed marked reduction of hepatic necrosis, serum marker enzymes and levels of tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-6 in BRP pretreated mice when compared with galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide-challenged mice. Mice pretreated with BRP decreased the activation of caspases-3 and caspase-8, and showed a reduced level of DNA fragmentation of liver cells. BRP also reduced hepatic lipid peroxidation, increased potential of hepatic antioxidative defense system, and reduced hepatic nitric oxide level which was elevated by galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide injection. Immunoblot analysis showed down-regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 proteins of liver tissues in BRP pretreated group when compared with galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide-challenged group. Furthermore, treatment with galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide markedly increased toll-like receptor 4, nuclear level of nuclear factor-κB, and phosphorylation of both extracellular signal-regulated kinase and c-Jun N-terminal kinase in liver tissues. However, these increases were attenuated by pretreatment with BRP. The results suggest that BRP alleviates galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide-induced liver injury by enhancing antioxidative defense system, suppressing inflammatory responses and reducing apoptotic signaling.
Keywords: Boschniakia rossica; hepatic failure; mice; polysaccharide.
Figures




References
-
- Kim SJ, Kim KM, Park J, Kwak JH, Kim YS, Lee SM. Geniposidic acid protects against D-galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide-induced hepatic failure in mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013;146:271–277. - PubMed
-
- Huang CC, Lin KJ, Cheng YW, Hsu UA, Yang SS, Shyur LF. Hepatoprotective effect and mechanistic insights of deoxyelephantopin, a phyto-sesquiterpene lactone, against fulminant hepatitis. J Nutr Biochem. 2013;24:516–530. - PubMed
-
- Ewaschuk J, Endersby R, Thiel D, et al. Probiotic bacteria prevent hepatic damage and maintain colonic barrier function in a mouse model of sepsis. Hepatology. 2007;46:841–850. - PubMed
-
- Kang JW, Kim DW, Choi JS, Kim YS, Lee SM. Scoparone attenuates D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide-induced fulminant hepatic failure through inhibition of toll-like receptor 4 signaling in mice. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013;57:132–139. - PubMed
-
- Wang YZ, Li YX, Xie JM, et al. Protective effects of probiotic Lactobacillus casei Zhang against endotoxin and d-galactosamine-induced liver injury in rats via anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory capacities. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013;15:30–37. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

