Impact of hemodialysis on dyspnea and lung function in end stage kidney disease patients
- PMID: 24895552
- PMCID: PMC4034396
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/212751
Impact of hemodialysis on dyspnea and lung function in end stage kidney disease patients
Abstract
Background: Respiratory symptoms are usually underestimated in patients with chronic kidney disease undergoing maintenance hemodialysis. Therefore, we set out to investigate the prevalence of patients chronic dyspnea and the relationship of the symptom to lung function indices.
Methods: Twenty-five clinically stable hemodialysis patients were included. The mMRC dyspnea scale was applied before and after hemodialysis. Spirometry, single breath nitrogen test, arterial blood gases, static maximum inspiratory (P(imax)) and expiratory (P(emax)) muscle pressures, and mouth occlusion pressure (P 0.1) were also measured.
Results: Despite normal spirometry, all patients (100%) reported mild to moderate degree of chronic dyspnea pre which was reduced after hemodialysis. The sole predictor of (Δ) mMRC was the (Δ) P 0.1 (r = 0.71, P < 0.001). The P(imax) was reduced before and correlated with the duration of hemodialysis (r = 0.614, P < 0.001), whilst after the session it was significantly increased (P < 0.001). Finally (Δ) weight was correlated with the (Δ) P(imax) %pred (r = 0.533, P = 0,006) and with the (Δ) CV (%pred) (r = 0.65, P < 0.001).
Conclusion: We conclude that dyspnea is the major symptom among the CKD patients that improves after hemodialysis. The neuromechanical dissociation observed probably is one of the major pathophysiologic mechanisms of dyspnea.
Figures
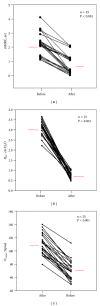
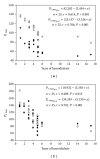


References
-
- Lazarus JM, Brenner BM. Chronic renal failure. In: Fauci AS, Braunwald E, Isselbacher K, et al., editors. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. 14th edition. New York, NY, USA: Mc Grow-Hill; 1998. pp. 1513–1520.
-
- Weisbord SD, Fried LF, Arnold RM, et al. Prevalence, severity, and importance of physical and emotional symptoms in chronic hemodialysis patients. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. 2005;16(8):2487–2494. - PubMed
-
- Merkus MP, Jager KJ, Dekker FW, De Haan RJ, Boeschoten EW, Krediet RT. Physical symptoms and quality of life in patients on chronic dialysis: results of the Netherlands Cooperative Study on Adequacy of Dialysis (NECOSAD) Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation. 1999;14(5):1163–1170. - PubMed
-
- Murtagh FEM, Addington-Hall J, Higginson IJ. The prevalence of symptoms in end-stage renal disease: a systematic review. Advances in Chronic Kidney Disease. 2007;14(1):82–99. - PubMed
-
- Wallin C-JB, Jacobson SH, Leksell LG. Subclinical pulmonary oedema and intermittent haemodialysis. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation. 1996;11(11):2269–2275. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

