Recanalization and clinical outcome of occlusion sites at baseline CT angiography in the Interventional Management of Stroke III trial
- PMID: 24895878
- PMCID: PMC4174723
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.14132649
Recanalization and clinical outcome of occlusion sites at baseline CT angiography in the Interventional Management of Stroke III trial
Abstract
Purpose: To use baseline computed tomographic (CT) angiography to analyze imaging and clinical end points in an Interventional Management of Stroke III cohort to identify patients who would benefit from endovascular stroke therapy.
Materials and methods: The primary clinical end point was 90-day dichotomized modified Rankin Scale (mRS) score. Secondary end points were 90-day mRS score distribution and 24-hour recanalization. Prespecified subgroup was baseline proximal occlusions (internal carotid, M1, or basilar arteries). Exploratory analyses were subsets with any occlusion and specific sites of occlusion (two-sided α = .01).
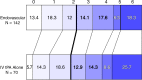
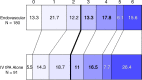
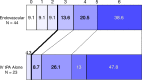
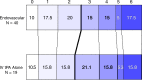
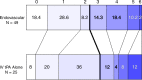
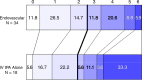
Results: Of 656 subjects, 306 (47%) underwent baseline CT angiography or magnetic resonance angiography. Of 306, 282 (92%) had arterial occlusions. At baseline CT angiography, proximal occlusions (n = 220) demonstrated no difference in primary outcome (41.3% [62 of 150] endovascular vs 38% [27 of 70] intravenous [IV] tissue-plasminogen activator [tPA]; relative risk, 1.07 [99% confidence interval: 0.67, 1.70]; P = .70); however, 24-hour recanalization rate was higher for endovascular treatment (n = 167; 84.3% [97 of 115] endovascular vs 56% [29 of 52] IV tPA; P < .001). Exploratory subgroup analysis for any occlusion at baseline CT angiography did not demonstrate significant differences between endovascular and IV tPA arms for primary outcome (44.7% [85 of 190] vs 38% [35 of 92], P = .29), although ordinal shift analysis of full mRS distribution demonstrated a trend toward more favorable outcome (P = .011). Carotid T- or L-type occlusion (terminal internal carotid artery [ICA] with M1 middle cerebral artery and/or A1 anterior cerebral artery involvement) or tandem (extracranial or intracranial) ICA and M1 occlusion subgroup also showed a trend favoring endovascular treatment over IV tPA alone for primary outcome (26% [12 of 46] vs 4% [one of 23], P = .047).
Conclusion: Significant differences were identified between treatment arms for 24-hour recanalization in proximal occlusions; carotid T- or L-type and tandem ICA and M1 occlusions showed greater recanalization and a trend toward better outcome with endovascular treatment. Vascular imaging should be mandated in future endovascular trials to identify such occlusions. Online supplemental material is available for this article.
© RSNA, 2014.
Figures
References
-
- De Silva DA, Brekenfeld C, Ebinger M, et al. . The benefits of intravenous thrombolysis relate to the site of baseline arterial occlusion in the Echoplanar Imaging Thrombolytic Evaluation Trial (EPITHET). Stroke 2010;41(2):295–299. - PubMed
-
- Dzialowski I, Puetz V, Buchan AM, Demchuk AM, Hill MD; Calgary Stroke Program. Does the application of x-ray contrast agents impair the clinical effect of intravenous recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator in acute ischemic stroke patients? Stroke 2012;43(6):1567–1571. - PubMed
-
- Dehmer GJ, Gresalfi N, Daly D, Oberhardt B, Tate DA. Impairment of fibrinolysis by streptokinase, urokinase and recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator in the presence of radiographic contrast agents. J Am Coll Cardiol 1995;25(5):1069–1075. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

