Plasma interleukin-27 (IL-27) levels are not modulated in patients with chronic HIV-1 infection
- PMID: 24896094
- PMCID: PMC4045808
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098989
Plasma interleukin-27 (IL-27) levels are not modulated in patients with chronic HIV-1 infection
Abstract
Objective: IL-27 is an immunomodulatory cytokine with potent anti-HIV properties in PBMCs, CD4+ T cells, macrophages and immature dendritic cells. Previous smaller studies have suggested that HIV-1 infection may alter IL-27 and influence HIV-1 pathogenesis. The aim of this study was to examine the relationship between plasma IL-27 levels in a well-characterised cohort of HIV-1 infected patients.
Methods: Patients were stratified into four groups based on HIV-1 viral load and matched according to age, gender and those receiving antiretroviral treatment. IL-27 levels and C-reactive protein (CRP) were measured using electrochemiluminescence assays. D-dimer and CD4+ T cell counts were measured using an Enzyme Linked Fluorescence Assay and FACS, respectively. sCD14 and sCD163 were measured using ELISA. HIV-1 viral load was measured by bDNA or qRT-PCR assays.
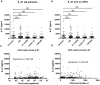
Results: Plasma IL-27 levels were measured in 505 patients (462 HIV+, 43 controls). The mean level (±SEM) of IL-27 in controls was 2990.7±682.1 pg/ml, in the <50 copies/ml group it was 2008.0±274.8 pg/ml, in the 51-10,000 copies group it was 1468.7±172.3 pg/ml, in the 10,001-100,000 copies/ml group it was 1237.9±127.3 pg/ml and in the >100,000 copies/ml group it was 1590.1±223.7 pg/ml. No statistically significant difference in IL-27 levels between groups were seen. There were no correlations noted between IL-27 and HIV-1 viral load or CD4+ T cell counts. There was a small correlation noted between D-dimer and IL-27 (Spearman r = 0.09, p = 0.03) and sCD163 and IL-27 (Spearman r = 0.12, p = 0.005). No correlation was observed between IL-27 and CRP or sCD14 levels.
Conclusions: This is the largest study examining the levels of plasma IL-27 in HIV-1 infection. While IL-27 levels are not significantly altered in HIV-1 infection compared to uninfected controls there may be a small association between IL-27 and D-dimer levels and IL-27 and sCD163 levels.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Pflanz S, Timans JC, Cheung J, Rosales R, Kanzler H, et al. (2002) IL-27, a heterodimeric cytokine composed of EBI3 and p28 protein, induces proliferation of naive CD4(+) T cells. Immunity 16: 779–790. - PubMed
-
- Batten M, Ghilardi N (2007) The biology and therapeutic potential of interleukin 27. J Mol Med (Berl) 85: 661–672. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

