Engineering a memory with LTD and LTP
- PMID: 24896183
- PMCID: PMC4210354
- DOI: 10.1038/nature13294
Engineering a memory with LTD and LTP
Abstract
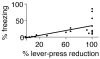
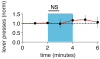
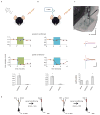
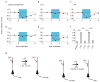
It has been proposed that memories are encoded by modification of synaptic strengths through cellular mechanisms such as long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD). However, the causal link between these synaptic processes and memory has been difficult to demonstrate. Here we show that fear conditioning, a type of associative memory, can be inactivated and reactivated by LTD and LTP, respectively. We began by conditioning an animal to associate a foot shock with optogenetic stimulation of auditory inputs targeting the amygdala, a brain region known to be essential for fear conditioning. Subsequent optogenetic delivery of LTD conditioning to the auditory input inactivates memory of the shock. Then subsequent optogenetic delivery of LTP conditioning to the auditory input reactivates memory of the shock. Thus, we have engineered inactivation and reactivation of a memory using LTD and LTP, supporting a causal link between these synaptic processes and memory.
Figures











References
-
- Squire LR, Kandel ER. Memory : from mind to molecules. 2. Roberts & Co; 2009.
-
- Stevens CF. A million dollar question: does LTP = memory? Neuron. 1998;20:1–2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

