Structure of the BTB domain of Keap1 and its interaction with the triterpenoid antagonist CDDO
- PMID: 24896564
- PMCID: PMC4045772
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098896
Structure of the BTB domain of Keap1 and its interaction with the triterpenoid antagonist CDDO
Abstract
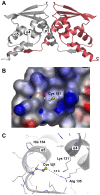
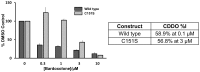
The protein Keap1 is central to the regulation of the Nrf2-mediated cytoprotective response, and is increasingly recognized as an important target for therapeutic intervention in a range of diseases involving excessive oxidative stress and inflammation. The BTB domain of Keap1 plays key roles in sensing environmental electrophiles and in mediating interactions with the Cul3/Rbx1 E3 ubiquitin ligase system, and is believed to be the target for several small molecule covalent activators of the Nrf2 pathway. However, despite structural information being available for several BTB domains from related proteins, there have been no reported crystal structures of Keap1 BTB, and this has precluded a detailed understanding of its mechanism of action and interaction with antagonists. We report here the first structure of the BTB domain of Keap1, which is thought to contain the key cysteine residue responsible for interaction with electrophiles, as well as structures of the covalent complex with the antagonist CDDO/bardoxolone, and of the constitutively inactive C151W BTB mutant. In addition to providing the first structural confirmation of antagonist binding to Keap1 BTB, we also present biochemical evidence that adduction of Cys 151 by CDDO is capable of inhibiting the binding of Cul3 to Keap1, and discuss how this class of compound might exert Nrf2 activation through disruption of the BTB-Cul3 interface.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Itoh K, Chiba T, Takahashi S, Ishii T, Igarashi K, et al. (1997) An Nrf2/small Maf heterodimer mediates the induction of phase II detoxifying enzyme genes through antioxidant response elements. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 236: 313–322. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

