Plasmin-dependent modulation of the blood-brain barrier: a major consideration during tPA-induced thrombolysis?
- PMID: 24896566
- PMCID: PMC4126105
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2014.99
Plasmin-dependent modulation of the blood-brain barrier: a major consideration during tPA-induced thrombolysis?
Abstract
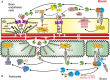
Plasmin, the principal downstream product of tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA), is known for its potent fibrin-degrading capacity but is also recognized for many non-fibrinolytic activities. Curiously, plasmin has not been conclusively linked to blood-brain barrier (BBB) disruption during recombinant tPA (rtPA)-induced thrombolysis in ischemic stroke. This is surprising given the substantial involvement of tPA in the modulation of BBB permeability and the co-existence of tPA and plasminogen in both blood and brain throughout the ischemic event. Here, we review the work that argues a role for plasmin together with endogenous tPA or rtPA in BBB alteration, presenting the overall controversy around the topic yet creating a rational case for an involvement of plasmin in this process.
Figures
References
-
- Collen D, Lijnen HR. Thrombolytic agents. Thromb Haemost. 2005;93:627–630. - PubMed
-
- Cesarman-Maus G, Hajjar KA. Molecular mechanisms of fibrinolysis. Br J Haematol. 2005;129:307–321. - PubMed
-
- Collen D, Lijnen HR. Tissue-type plasminogen activator: a historical perspective and personal account. J Thromb Haemost. 2004;2:541–546. - PubMed
-
- NINDS trial Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:1581–1587. - PubMed
-
- Hacke W, Kaste M, Bluhmki E, Brozman M, Davalos A, Guidetti D, et al. Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 hours after acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1317–1329. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

