Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNAs (EBERs) are present in fractions related to exosomes released by EBV-transformed cells
- PMID: 24896633
- PMCID: PMC4045842
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099163
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNAs (EBERs) are present in fractions related to exosomes released by EBV-transformed cells
Abstract
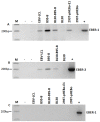
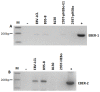
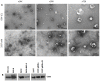
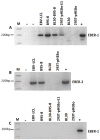
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is an oncogenic herpesvirus associated with a number of human malignancies of epithelial and lymphoid origin. However, the mechanism of oncogenesis is unclear. A number of viral products, including EBV latent proteins and non-protein coding RNAs have been implicated. Recently it was reported that EBV-encoded small RNAs (EBERs) are released from EBV infected cells and they can induce biological changes in cells via signaling from toll-like receptor 3. Here, we investigated if these abundantly expressed non-protein coding EBV RNAs (EBER-1 and EBER-2) are excreted from infected cells in exosomal fractions. Using differential ultracentrifugation we isolated exosomes from three EBV positive cell lines (B95-8, EBV-LCL, BL30-B95-8), one EBER-1 transfected cell line (293T-pHEBo-E1) and two EBV-negative cell lines (BL30, 293T-pHEBo). The identity of purified exosomes was determined by electron microscopy and western blotting for CD63. The presence of EBERs in cells, culture supernatants and purified exosomal fractions was determined using RT-PCR and confirmed by sequencing. Purified exosomal fractions were also tested for the presence of the EBER-1-binding protein La, using western blotting. Both EBER-1 and EBER-2 were found to be present not only in the culture supernatants, but also in the purified exosome fractions of all EBV-infected cell lines. EBER-1 could also be detected in exosomal fractions from EBER-1 transfected 293T cells whilst the fractions from vector only transfectants were clearly negative. Furthermore, purified exosomal fractions also contained the EBER-binding protein (La), supporting the notion that EBERs are most probably released from EBV infected cells in the form of EBER-La complex in exosomes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multifunctional non-coding Epstein-Barr virus encoded RNAs (EBERs) contribute to viral pathogenesis.Virus Res. 2016 Jan 2;212:30-8. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2015.08.007. Epub 2015 Aug 18. Virus Res. 2016. PMID: 26292159 Review.
-
Critical role of Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)-encoded RNA in efficient EBV-induced B-lymphocyte growth transformation.J Virol. 2005 Apr;79(7):4298-307. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.7.4298-4307.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15767430 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and Characterization of Exosomes Released by EBV-Immortalized Cells.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1532:147-158. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6655-4_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27873273
-
The labyrinth of interactions of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNAs.Rev Med Virol. 2014 Jan;24(1):3-14. doi: 10.1002/rmv.1763. Epub 2013 Sep 18. Rev Med Virol. 2014. PMID: 24105992 Review.
-
Tracking EBV-encoded RNAs (EBERs) from the nucleus to the excreted exosomes of B-lymphocytes.Sci Rep. 2018 Oct 18;8(1):15438. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-33758-4. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30337610 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Epstein-Barr virus is present in the brain of most cases of multiple sclerosis and may engage more than just B cells.PLoS One. 2018 Feb 2;13(2):e0192109. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192109. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29394264 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Extracellular Vesicles as Allies of HIV, HCV and SARS Viruses.Viruses. 2020 May 22;12(5):571. doi: 10.3390/v12050571. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32456011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viruses in colorectal cancer.Mol Oncol. 2022 Apr;16(7):1423-1450. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13100. Epub 2021 Sep 30. Mol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34514694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune Escape by Non-coding RNAs of the Epstein Barr Virus.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jun 21;12:657387. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.657387. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34234755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral noncoding RNAs: more surprises.Genes Dev. 2015 Mar 15;29(6):567-84. doi: 10.1101/gad.259077.115. Genes Dev. 2015. PMID: 25792595 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Henderson E, Miller G, Robinson J, Heston L (1977) Efficiency of transformation of lymphocytes by Epstein-Barr virus. Virology 76: 152–163. - PubMed
-
- Kieff E, Rickinson AB (2007) Epstein-Barr Virus and its Replication. In: Knipe, D.M, Howley, P.M., editors. Fields Virology.Walters Kluwer/Lippincott. pp. 2603–2654.
-
- Wang D, Liebowitz D, Kieff E (1985) An EBV membrane protein expressed in immortalized lymphocytes transforms established rodent cells. Cell 43: 831–840. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

