Phenotype standardization for statin-induced myotoxicity
- PMID: 24897241
- PMCID: PMC4172546
- DOI: 10.1038/clpt.2014.121
Phenotype standardization for statin-induced myotoxicity
Abstract
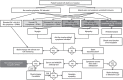
Statins are widely used lipid-lowering drugs that are effective in reducing cardiovascular disease risk. Although they are generally well tolerated, they can cause muscle toxicity, which can lead to severe rhabdomyolysis. Research in this area has been hampered to some extent by the lack of standardized nomenclature and phenotypic definitions. We have used numerical and descriptive classifications and developed an algorithm to define statin-related myotoxicity phenotypes, including myalgia, myopathy, rhabdomyolysis, and necrotizing autoimmune myopathy.
Figures
References
-
- Law M., Rudnicka A.R. Statin safety: a systematic review. Am. J. Cardiol. 2006;97:52C–60C. - PubMed
-
- Sathasivam S. Statin induced myotoxicity. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2012;23:317–324. - PubMed
-
- Stone N.J., et al. 2013 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Treatment of Blood Cholesterol to Reduce Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Risk in Adults: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines Circulation 2013. e-pub ahead of print 12 November 2013.
-
- Graham D.J., et al. Incidence of hospitalized rhabdomyolysis in patients treated with lipid-lowering drugs. JAMA. 2004;292:2585–2590. - PubMed
-
- Staffa J.A., Chang J., Green L. Cerivastatin and reports of fatal rhabdomyolysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002;346:539–540. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

