Catalytic activity of cGMP-dependent protein kinase type I in intact cells is independent of N-terminal autophosphorylation
- PMID: 24897423
- PMCID: PMC4045857
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098946
Catalytic activity of cGMP-dependent protein kinase type I in intact cells is independent of N-terminal autophosphorylation
Abstract
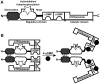
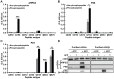
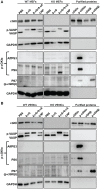
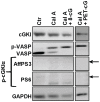
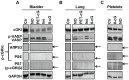
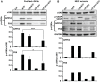
Although cGMP-dependent protein kinase type I (cGKI) is an important mediator of cGMP signaling and upcoming drug target, its in vivo-biochemistry is not well understood. Many studies showed that purified cGKI autophosphorylates multiple sites at its N-terminus. Autophosphorylation might be involved in kinase activation, but it is unclear whether this happens also in intact cells. To study cGKI autophosphorylation in vitro and in vivo, we have generated phospho-specific antisera against major in vitro-autophosphorylation sites of the cGKI isoforms, cGKIα and cGKIβ. These antisera detected specifically and with high sensitivity phospho-cGKIα (Thr58), phospho-cGKIα (Thr84), or phospho-cGKIβ (Thr56/Ser63/Ser79). Using these antisera, we show that ATP-induced autophosphorylation of cGKI in purified preparations and cell extracts did neither require nor induce an enzyme conformation capable of substrate heterophosphorylation; it was even inhibited by pre-incubation with cGMP. Interestingly, phospho-cGKI species were not detectable in intact murine cells and tissues, both under basal conditions and after induction of cGKI catalytic activity. We conclude that N-terminal phosphorylation, although readily induced in vitro, is not required for the catalytic activity of cGKIα and cGKIβ in vivo. These results will also inform screening strategies to identify novel cGKI modulators.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
H₂O₂ lowers the cytosolic Ca²⁺ concentration via activation of cGMP-dependent protein kinase Iα.Free Radic Biol Med. 2012 Oct 15;53(8):1574-83. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.08.011. Epub 2012 Aug 15. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012. PMID: 22922339
-
Functional reconstitution of vascular smooth muscle cells with cGMP-dependent protein kinase I isoforms.Circ Res. 2002 May 31;90(10):1080-6. doi: 10.1161/01.res.0000019586.95768.40. Circ Res. 2002. PMID: 12039797
-
Alternative splicing of cGMP-dependent protein kinase I in angiotensin-hypertension: novel mechanism for nitrate tolerance in vascular smooth muscle.Circ Res. 2003 Oct 31;93(9):805-12. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000097872.69043.A0. Epub 2003 Sep 25. Circ Res. 2003. PMID: 14512447
-
Targets of cGMP/cGKI in Cardiac Myocytes.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2020 Jun;75(6):494-507. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000817. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32168155 Review.
-
Function of cGMP-dependent protein kinases in the nervous system.Rev Neurosci. 2005;16(1):23-41. doi: 10.1515/revneuro.2005.16.1.23. Rev Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15810652 Review.
Cited by
-
Angiotensin II-induced cardiac fibrosis and dysfunction are exacerbated by deletion of cGKI in periostin+ myofibroblasts.Clin Sci (Lond). 2025 Apr 23;139(11):507-26. doi: 10.1042/CS20241204. Online ahead of print. Clin Sci (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40267335 Free PMC article.
-
Detection and Characterization of Phosphorylation, Glycosylation, and Fatty Acid Bound to Fetuin A in Human Blood.J Clin Med. 2021 Jan 22;10(3):411. doi: 10.3390/jcm10030411. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33499061 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing the Protein Isoforms of foraging (for), the PKGI Ortholog in Drosophila melanogaster.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 16;24(12):10219. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210219. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373366 Free PMC article.
-
A substitution in cGMP-dependent protein kinase 1 associated with aortic disease induces an active conformation in the absence of cGMP.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jul 24;295(30):10394-10405. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.010984. Epub 2020 Jun 5. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32506052 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beavo JA, Brunton LL (2002) Cyclic nucleotide research — still expanding after half a century. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3: 710–718. - PubMed
-
- Kemp-Harper B, Feil R (2008) Meeting report: cGMP matters. Sci Signal 1: pe12. - PubMed
-
- Feil R, Lohmann SM, de Jonge H, Walter U, Hofmann F (2003) Cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinases and the cardiovascular system: insights from genetically modified mice. Circ Res 93: 907–916. - PubMed
-
- Hofmann F, Feil R, Kleppisch T, Schlossmann J (2006) Function of cGMP-dependent protein kinases as revealed by gene deletion. Physiol Rev 86: 1–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

