Undesired small RNAs originate from an artificial microRNA precursor in transgenic petunia (Petunia hybrida)
- PMID: 24897430
- PMCID: PMC4045805
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098783
Undesired small RNAs originate from an artificial microRNA precursor in transgenic petunia (Petunia hybrida)
Abstract
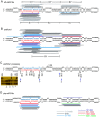
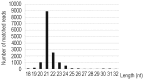
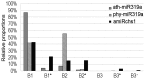
Although artificial microRNA (amiRNA) technology has been used frequently in gene silencing in plants, little research has been devoted to investigating the accuracy of amiRNA precursor processing. In this work, amiRNAchs1 (amiRchs1), based on the Arabidopsis miR319a precursor, was expressed in order to suppress the expression of CHS genes in petunia. The transgenic plants showed the CHS gene-silencing phenotype. A modified 5' RACE technique was used to map small-RNA-directed cleavage sites and to detect processing intermediates of the amiRchs1 precursor. The results showed that the target CHS mRNAs were cut at the expected sites and that the amiRchs1 precursor was processed from loop to base. The accumulation of small RNAs in amiRchs1 transgenic petunia petals was analyzed using the deep-sequencing technique. The results showed that, alongside the accumulation of the desired artificial microRNAs, additional small RNAs that originated from other regions of the amiRNA precursor were also accumulated at high frequency. Some of these had previously been found to be accumulated at low frequency in the products of ath-miR319a precursor processing and some of them were accompanied by 3'-tailing variant. Potential targets of the undesired small RNAs were discovered in petunia and other Solanaceae plants. The findings draw attention to the potential occurrence of undesired target silencing induced by such additional small RNAs when amiRNA technology is used. No appreciable production of secondary small RNAs occurred, despite the fact that amiRchs1 was designed to have perfect complementarity to its CHS-J target. This confirmed that perfect pairing between an amiRNA and its targets is not the trigger for secondary small RNA production. In conjunction with the observation that amiRNAs with perfect complementarity to their target genes show high efficiency and specificity in gene silencing, this finding has an important bearing on future applications of amiRNAs in gene silencing in plants.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Investigation of a miRNA-Induced Gene Silencing Technique in Petunia Reveals Alterations in miR173 Precursor Processing and the Accumulation of Secondary siRNAs from Endogenous Genes.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 14;10(12):e0144909. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144909. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26658695 Free PMC article.
-
Tandemly arranged chalcone synthase A genes contribute to the spatially regulated expression of siRNA and the natural bicolor floral phenotype in Petunia hybrida.Plant J. 2012 Jun;70(5):739-49. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2012.04908.x. Epub 2012 Mar 30. Plant J. 2012. PMID: 22288551
-
Engineered Artificial MicroRNA Precursors Facilitate Cloning and Gene Silencing in Arabidopsis and Rice.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 10;20(22):5620. doi: 10.3390/ijms20225620. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31717686 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial microRNAs (amiRNAs) engineering - On how microRNA-based silencing methods have affected current plant silencing research.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 Mar 18;406(3):315-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.02.045. Epub 2011 Feb 15. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011. PMID: 21329663 Review.
-
Artificial microRNA mediated gene silencing in plants: progress and perspectives.Plant Mol Biol. 2014 Sep;86(1-2):1-18. doi: 10.1007/s11103-014-0224-7. Epub 2014 Jul 15. Plant Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 25022825 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigation of a miRNA-Induced Gene Silencing Technique in Petunia Reveals Alterations in miR173 Precursor Processing and the Accumulation of Secondary siRNAs from Endogenous Genes.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 14;10(12):e0144909. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144909. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26658695 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeted mutation reveals a role for AN4 rather than DPL in regulating venation formation in the corolla tube of Petunia hybrida.Hortic Res. 2021 Jun 1;8(1):116. doi: 10.1038/s41438-021-00555-6. Hortic Res. 2021. PMID: 34059660 Free PMC article.
-
A high-efficiency gene silencing in plants using two-hit asymmetrical artificial MicroRNAs.Plant Biotechnol J. 2023 Sep;21(9):1799-1811. doi: 10.1111/pbi.14091. Epub 2023 Jul 1. Plant Biotechnol J. 2023. PMID: 37392408 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial microRNA-derived resistance to Cassava brown streak disease.J Virol Methods. 2016 May;231:38-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2016.02.004. Epub 2016 Feb 18. J Virol Methods. 2016. PMID: 26912232 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Applications of Artificial MicroRNA-Mediated Gene Silencing in Plant Biotechnology.Noncoding RNA. 2025 Mar 2;11(2):19. doi: 10.3390/ncrna11020019. Noncoding RNA. 2025. PMID: 40126343 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

