The impact of dietary isoflavonoids on malignant brain tumors
- PMID: 24898306
- PMCID: PMC4303154
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.265
The impact of dietary isoflavonoids on malignant brain tumors
Abstract
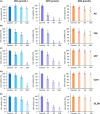
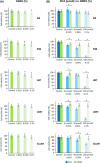
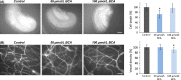
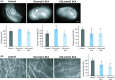
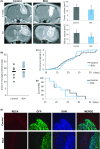
Poor prognosis and limited therapeutic options render malignant brain tumors one of the most devastating diseases in clinical medicine. Current treatment strategies attempt to expand the therapeutic repertoire through the use of multimodal treatment regimens. It is here that dietary fibers have been recently recognized as a supportive natural therapy in augmenting the body's response to tumor growth. Here, we investigated the impact of isoflavonoids on primary brain tumor cells. First, we treated glioma cell lines and primary astrocytes with various isoflavonoids and phytoestrogens. Cell viability in a dose-dependent manner was measured for biochanin A (BCA), genistein (GST), and secoisolariciresinol diglucoside (SDG). Dose-response action for the different isoflavonoids showed that BCA is highly effective on glioma cells and nontoxic for normal differentiated brain tissues. We further investigated BCA in ex vivo and in vivo experimentations. Organotypic brain slice cultures were performed and treated with BCA. For in vivo experiments, BCA was intraperitoneal injected in tumor-implanted Fisher rats. Tumor size and edema were measured and quantified by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans. In vascular organotypic glioma brain slice cultures (VOGIM) we found that BCA operates antiangiogenic and neuroprotective. In vivo MRI scans demonstrated that administered BCA as a monotherapy was effective in reducing significantly tumor-induced brain edema and showed a trend for prolonged survival. Our results revealed that dietary isoflavonoids, in particular BCA, execute toxicity toward glioma cells, antiangiogenic, and coevally neuroprotective properties, and therefore augment the range of state-of-the-art multimodal treatment approach.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; experimental therapeutics; microenvironment; nutrition.
© 2014 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Biochanin A inhibits endothelial cell functions and proangiogenic pathways: implications in glioma therapy.Anticancer Drugs. 2015 Mar;26(3):323-30. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000189. Anticancer Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25501542
-
Sunitinib impedes brain tumor progression and reduces tumor-induced neurodegeneration in the microenvironment.Cancer Sci. 2015 Feb;106(2):160-70. doi: 10.1111/cas.12580. Epub 2015 Feb 15. Cancer Sci. 2015. PMID: 25458015 Free PMC article.
-
A versatile ex vivo technique for assaying tumor angiogenesis and microglia in the brain.Oncotarget. 2016 Jan 12;7(2):1838-53. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6550. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26673818 Free PMC article.
-
Antiangiogenic therapy in malignant glioma: promise and challenge.Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13(35):3545-58. doi: 10.2174/138161207782794130. Curr Pharm Des. 2007. PMID: 18220791 Review.
-
Antiangiogenic therapy in brain tumor models.J Neurooncol. 1999;45(3):247-55. doi: 10.1023/a:1006395802727. J Neurooncol. 1999. PMID: 10845396 Review.
Cited by
-
Neobavaisoflavone May Modulate the Activity of Topoisomerase Inhibitors towards U-87 MG Cells: An In Vitro Study.Molecules. 2021 Jul 27;26(15):4516. doi: 10.3390/molecules26154516. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34361668 Free PMC article.
-
Perspectives Regarding the Role of Biochanin A in Humans.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Jul 12;10:793. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00793. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31354500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biochanin A Sensitizes Glioblastoma to Temozolomide by Inhibiting Autophagy.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Feb;59(2):1262-1272. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02674-6. Epub 2022 Jan 4. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 34981417
-
A novel approach to glioblastoma multiforme treatment using modulation of key pathways by naturally occurring small molecules.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Mar;33(3):1237-1254. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01666-5. Epub 2025 Feb 16. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 39955698 Review.
-
Antioxidants in brain tumors: current therapeutic significance and future prospects.Mol Cancer. 2022 Oct 28;21(1):204. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01668-9. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36307808 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

