New clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat locus spacer pair typing method based on the newly incorporated spacer for Salmonella enterica
- PMID: 24899040
- PMCID: PMC4136180
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00696-14
New clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat locus spacer pair typing method based on the newly incorporated spacer for Salmonella enterica
Abstract
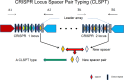
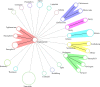
A clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat (CRISPR) typing method has recently been developed and used for typing and subtyping of Salmonella spp., but it is complicated and labor intensive because it has to analyze all spacers in two CRISPR loci. Here, we developed a more convenient and efficient method, namely, CRISPR locus spacer pair typing (CLSPT), which only needs to analyze the two newly incorporated spacers adjoining the leader array in the two CRISPR loci. We analyzed a CRISPR array of 82 strains belonging to 21 Salmonella serovars isolated from humans in different areas of China by using this new method. We also retrieved the newly incorporated spacers in each CRISPR locus of 537 Salmonella isolates which have definite serotypes in the Pasteur Institute's CRISPR Database to evaluate this method. Our findings showed that this new CLSPT method presents a high level of consistency (kappa = 0.9872, Matthew's correlation coefficient = 0.9712) with the results of traditional serotyping, and thus, it can also be used to predict serotypes of Salmonella spp. Moreover, this new method has a considerable discriminatory power (discriminatory index [DI] = 0.8145), comparable to those of multilocus sequence typing (DI = 0.8088) and conventional CRISPR typing (DI = 0.8684). Because CLSPT only costs about $5 to $10 per isolate, it is a much cheaper and more attractive method for subtyping of Salmonella isolates. In conclusion, this new method will provide considerable advantages over other molecular subtyping methods, and it may become a valuable epidemiologic tool for the surveillance of Salmonella infections.
Copyright © 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CRISPR-MVLST subtyping of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovars Typhimurium and Heidelberg and application in identifying outbreak isolates.BMC Microbiol. 2013 Nov 12;13:254. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-13-254. BMC Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24219629 Free PMC article.
-
Novel virulence gene and clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat (CRISPR) multilocus sequence typing scheme for subtyping of the major serovars of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011 Mar;77(6):1946-56. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02625-10. Epub 2011 Jan 28. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21278266 Free PMC article.
-
CSESA: an R package to predict Salmonella enterica serotype based on newly incorporated spacer pairs of CRISPR.BMC Bioinformatics. 2019 Apr 27;20(1):215. doi: 10.1186/s12859-019-2806-5. BMC Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 31029079 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPRs: molecular signatures used for pathogen subtyping.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014 Jan;80(2):430-9. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02790-13. Epub 2013 Oct 25. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24162568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multilocus variable number tandem repeat analysis for Salmonella enterica subspecies.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011 Apr;30(4):465-73. doi: 10.1007/s10096-010-1110-0. Epub 2010 Dec 11. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21153561 Review.
Cited by
-
CRISPR Typing of Clinical Strains of Salmonella spp. Isolated in Tehran, Iran.Iran J Public Health. 2023 Aug;52(8):1758-1763. doi: 10.18502/ijph.v52i8.13415. Iran J Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37744550 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Resistance and CRISPR Typing Among Salmonella Isolates From Poultry Farms in China.Front Microbiol. 2021 Sep 16;12:730046. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.730046. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34603259 Free PMC article.
-
Utilization of Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats to Genotype Escherichia coli Serogroup O80.Front Microbiol. 2020 Jul 23;11:1708. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01708. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32793166 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial CRISPR Regions: General Features and their Potential for Epidemiological Molecular Typing Studies.Open Microbiol J. 2018 Apr 23;12:59-70. doi: 10.2174/1874285801812010059. eCollection 2018. Open Microbiol J. 2018. PMID: 29755603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global MLST of Salmonella Typhi Revisited in Post-genomic Era: Genetic Conservation, Population Structure, and Comparative Genomics of Rare Sequence Types.Front Microbiol. 2016 Mar 2;7:270. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00270. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26973639 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Popoff M, Le Minor L. 2001. Antigenic formulas of the Salmonella serovars, 8th ed. WHO Collaborating Centre for Reference and Research on Salmonella, World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland
-
- Grimont PA, Weill F-X. 2007. Antigenic formulae of the Salmonella serovars, 9th ed. WHO Collaborating Centre for Reference and Research on Salmonella, Institut Pasteur, Paris, France: http://www.pasteur.fr/ip/portal/action/WebdriveActionEvent/oid/01s-00003...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

