Emerging targeted therapies for melanoma treatment (review)
- PMID: 24899250
- PMCID: PMC4091965
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2481
Emerging targeted therapies for melanoma treatment (review)
Abstract
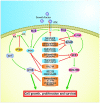
Cutaneous melanoma is an aggressive cancer with a poor prognosis for patients with advanced disease. The identification of several key molecular pathways implicated in the pathogenesis of melanoma has led to the development of novel therapies for this devastating disease. In melanoma, both the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK (MAPK) and the PI3K/AKT (AKT) signalling pathways are constitutively activated through multiple mechanisms. Targeting various effectors of these pathways with pharmacologic inhibitors may inhibit melanoma cell growth and angiogenesis. Ongoing clinical trials provide hope to improve progression-free survival of patients with advanced melanoma. This review summarizes the most relevant studies focused on the specific action of these new molecular targeted agents. Mechanisms of resistance to therapy are also discussed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms and strategies to overcome resistance to molecularly targeted therapy for melanoma.Cancer. 2017 Jun 1;123(S11):2118-2129. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30435. Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28543695 Review.
-
Targeting RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling in metastatic melanoma.IUBMB Life. 2013 Sep;65(9):748-58. doi: 10.1002/iub.1193. Epub 2013 Jul 29. IUBMB Life. 2013. PMID: 23893853 Review.
-
Melanoma: molecular pathogenesis and emerging target therapies (Review).Int J Oncol. 2009 Jun;34(6):1481-9. doi: 10.3892/ijo_00000277. Int J Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19424565 Review.
-
[Future targeting of the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathway in oncology: the example of melanoma].Bull Acad Natl Med. 2014 Feb;198(2):321-36; discussion 337-8. Bull Acad Natl Med. 2014. PMID: 26263707 French.
-
Drug resistance of BRAF-mutant melanoma: Review of up-to-date mechanisms of action and promising targeted agents.Eur J Pharmacol. 2019 Nov 5;862:172621. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172621. Epub 2019 Aug 22. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31446019 Review.
Cited by
-
Estrogen Receptor β in Melanoma: From Molecular Insights to Potential Clinical Utility.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2016 Oct 26;7:140. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2016.00140. eCollection 2016. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2016. PMID: 27833586 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rendomab B4, a monoclonal antibody that discriminates the human endothelin B receptor of melanoma cells and inhibits their migration.MAbs. 2016 Oct;8(7):1371-1385. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2016.1208865. Epub 2016 Jul 8. MAbs. 2016. PMID: 27390909 Free PMC article.
-
Evolving impact of long-term survival results on metastatic melanoma treatment.J Immunother Cancer. 2020 Oct;8(2):e000948. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-000948. J Immunother Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33037115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated analysis of multidimensional omics data on cutaneous melanoma prognosis.Genomics. 2016 Jun;107(6):223-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2016.04.005. Epub 2016 Apr 30. Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27141884 Free PMC article.
-
Growth Hormone Receptor Knockdown Sensitizes Human Melanoma Cells to Chemotherapy by Attenuating Expression of ABC Drug Efflux Pumps.Horm Cancer. 2017 Jun;8(3):143-156. doi: 10.1007/s12672-017-0292-7. Epub 2017 Mar 14. Horm Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28293855 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bataille V, Winnett A, Sasieni P, Newton Bishop JA, Cuzick J. Exposure to the sun and sunbeds and the risk of cutaneous melanoma in the UK: a case-control study. Eur J Cancer. 2004;40:429–435. - PubMed
-
- Hodis E, Watson IR, Kryukov GV, Arold ST, Imielinski M, Theurillat JP, Nickerson E, Auclair D, Li L, Place C, Dicara D, Ramos AH, Lawrence MS, Cibulskis K, Sivachenko A, Voet D, Saksena G, Stransky N, Onofrio RC, Winckler W, Ardlie K, Wagle N, Wargo J, Chong K, Morton DL, Stemke-Hale K, Chen G, Noble M, Meyerson M, Ladbury JE, Davies MA, Gershenwald JE, Wagner SN, Hoon DS, Schadendorf D, Lander ES, Gabriel SB, Getz G, Garraway LA, Chin L. A landscape of driver mutations in melanoma. Cell. 2012;150:251–263. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Thomas NE, Berwick M, Cordeiro-Stone M. Could BRAF mutations in melanocytic lesions arise from DNA damage induced by ultraviolet radiation? J Invest Dermatol. 2006;126:1693–1696. - PubMed
-
- Thomas NE, Edmiston SN, Alexander A, Millikan RC, Groben PA, Hao H, Tolbert D, Berwick M, Busam K, Begg CB, Mattingly D, Ollila DW, Tse CK, Hummer A, Lee-Taylor J, Conway K. Number of nevi and early-life ambient UV exposure are associated with BRAF-mutant melanoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2007;16:991–997. - PubMed
-
- Venesio T, Chiorino G, Balsamo A, Zaccagna A, Petti C, Scatolini M, Pisacane A, Sarotto I, Picciotto F, Risio M. In melanocytic lesions the fraction of BRAFV600Ealleles is associated with sun exposure but unrelated to ERK phosphorylation. Mod Pathol. 2008;21:716–726. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous