The role of hepatic lipids in hepatic insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 24899308
- PMCID: PMC4489847
- DOI: 10.1038/nature13478
The role of hepatic lipids in hepatic insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes
Abstract
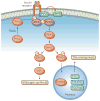
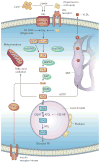
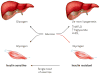
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its downstream sequelae, hepatic insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes, are rapidly growing epidemics, which lead to increased morbidity and mortality rates, and soaring health-care costs. Developing interventions requires a comprehensive understanding of the mechanisms by which excess hepatic lipid develops and causes hepatic insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Proposed mechanisms implicate various lipid species, inflammatory signalling and other cellular modifications. Studies in mice and humans have elucidated a key role for hepatic diacylglycerol activation of protein kinase Cε in triggering hepatic insulin resistance. Therapeutic approaches based on this mechanism could alleviate the related epidemics of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Browning JD, et al. Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in an urban population in the United States: impact of ethnicity. Hepatology. 2004;40:1387–1395. - PubMed
-
- Smits MM, Ioannou GN, Boyko EJ, Utzschneider KM. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease as an independent manifestation of the metabolic syndrome: results of a US national survey in three ethnic groups. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;28:664–670. - PubMed
-
- Fan JG, et al. Prevalence of and risk factors for fatty liver in a general population of Shanghai, China. J Hepatol. 2005;43:508–514. - PubMed
-
- Amarapurkar DN, et al. How common is non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in the Asia-Pacific region and are there local differences? J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;22:788–793. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 RR024139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK-40936/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK-085836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX000901/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- P30 DK-45735/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK040936/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32-DK101019/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023686/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK045735/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK-059635/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK-49230/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK034989/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG-23686/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK101019/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK049230/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R13 DK085836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR-024139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK059635/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

