miR-34/449 miRNAs are required for motile ciliogenesis by repressing cp110
- PMID: 24899310
- PMCID: PMC4119886
- DOI: 10.1038/nature13413
miR-34/449 miRNAs are required for motile ciliogenesis by repressing cp110
Abstract
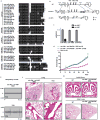
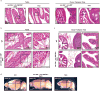
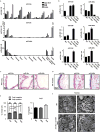
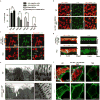
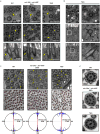
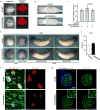
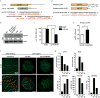
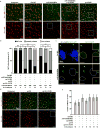
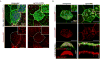
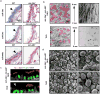
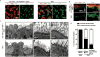
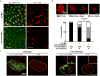
The mir-34/449 family consists of six homologous miRNAs at three genomic loci. Redundancy of miR-34/449 miRNAs and their dominant expression in multiciliated epithelia suggest a functional significance in ciliogenesis. Here we report that mice deficient for all miR-34/449 miRNAs exhibited postnatal mortality, infertility and strong respiratory dysfunction caused by defective mucociliary clearance. In both mouse and Xenopus, miR-34/449-deficient multiciliated cells (MCCs) exhibited a significant decrease in cilia length and number, due to defective basal body maturation and apical docking. The effect of miR-34/449 on ciliogenesis was mediated, at least in part, by post-transcriptional repression of Cp110, a centriolar protein suppressing cilia assembly. Consistent with this, cp110 knockdown in miR-34/449-deficient MCCs restored ciliogenesis by rescuing basal body maturation and docking. Altogether, our findings elucidate conserved cellular and molecular mechanisms through which miR-34/449 regulate motile ciliogenesis.
Figures

Comment in
-
Cell biology: Short RNAs and shortness of breath.Nature. 2014 Jun 5;510(7503):40-2. doi: 10.1038/510040a. Nature. 2014. PMID: 24899299 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
-
- He L, Hannon GJ. MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:522–31. - PubMed
-
- Kim VN. Small RNAs: classification, biogenesis, and function. Mol Cells. 2005;19:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Du T, Zamore PD. microPrimer: the biogenesis and function of microRNA. Development. 2005;132:4645–4652. - PubMed
-
- Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75:843–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

