Associations of objectively and subjectively measured sleep quality with subsequent cognitive decline in older community-dwelling men: the MrOS sleep study
- PMID: 24899757
- PMCID: PMC4044750
- DOI: 10.5665/sleep.3562
Associations of objectively and subjectively measured sleep quality with subsequent cognitive decline in older community-dwelling men: the MrOS sleep study
Abstract
Study objectives: To examine associations of objectively and subjectively measured sleep with subsequent cognitive decline.
Design: A population-based longitudinal study.
Setting: Six centers in the United States.
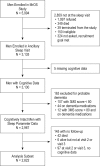
Participants: Participants were 2,822 cognitively intact community-dwelling older men (mean age 76.0 ± 5.3 y) followed over 3.4 ± 0.5 y.
Interventions: None.
Measurements and results: OBJECTIVELY MEASURED SLEEP PREDICTORS FROM WRIST ACTIGRAPHY: total sleep time (TST), sleep efficiency (SE), wake after sleep onset (WASO), number of long wake episodes (LWEP). Self-reported sleep predictors: sleep quality (Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index [PSQI]), daytime sleepiness (Epworth Sleepiness Scale [ESS]), TST. Clinically significant cognitive decline: five-point decline on the Modified Mini-Mental State examination (3MS), change score for the Trails B test time in the worse decile. Associations of sleep predictors and cognitive decline were examined with logistic regression and linear mixed models. After multivariable adjustment, higher levels of WASO and LWEP and lower SE were associated with an 1.4 to 1.5-fold increase in odds of clinically significant decline (odds ratio 95% confidence interval) Trails B test: SE < 70% versus SE ≥ 70%: 1.53 (1.07, 2.18); WASO ≥ 90 min versus WASO < 90 min: 1.47 (1.09, 1.98); eight or more LWEP versus fewer than eight: 1.38 (1.02, 1.86). 3MS: eight or more LWEP versus fewer than eight: 1.36 (1.09, 1.71), with modest relationships to linear change in cognition over time. PSQI was related to decline in Trails B performance (3 sec/y per standard deviation increase).
Conclusions: Among older community-dwelling men, reduced sleep efficiency, greater nighttime wakefulness, greater number of long wake episodes, and poor self-reported sleep quality were associated with subsequent cognitive decline.
Keywords: Aging; cognitive function; disturbed sleep; total sleep time.
Figures
References
-
- Foley D, Ancoli-Israel S, Britz P, et al. Sleep disturbances and chronic disease in older adults: results of the 2003 National Sleep Foundation Sleep in America Survey. J Psychosom Res. 2004;56:497–502. - PubMed
-
- Ott A, Breteler MM, van Harskamp F, et al. Incidence and risk of dementia. The Rotterdam Study. Am J Epidemiol. 1998;147:574–80. - PubMed
-
- Blackwell T, Yaffe K, Ancoli-Israel S, et al. Poor sleep is associated with impaired cognitive function in older women: the study of osteoporotic fractures. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2006;61:405–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 AR45632/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070848/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071194/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070847/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024140/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR45647/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR45654/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070838/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR45583/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070839/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR45580/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG027810/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070837/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR066160/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070842/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG042124/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR45614/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG042145/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG042168/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AG027810/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070841/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AG031155/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG18197/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG018197/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical