Overexpression of interleukin-23 and interleukin-17 in the lesion of pemphigus vulgaris: a preliminary study
- PMID: 24899786
- PMCID: PMC4037576
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/463928
Overexpression of interleukin-23 and interleukin-17 in the lesion of pemphigus vulgaris: a preliminary study
Abstract
IL-23/IL-17 axis has been identified as major factor involved in the pathogenesis of several autoimmune diseases; yet its pathogenetic role in pemphigus vulgaris (PV) remains controversial. The aim of this research was to investigate the potential role of IL-23/IL-17 axis in the immunopathogenesis of PV, and correlation between IL-23+ cells and IL-17+ cells was also evaluated. For this purpose, ten patients with PV, three patients with pemphigus foliaceus (PF), and six healthy individuals were allocated to this research. The lesional skin biopsy specimens were obtained before treatment. Then immunofluorescence staining was performed to analyze the expression of IL-23 and IL-17 in the PV/PF patients and the healthy individuals. The results showed that the numbers of IL-23+ and IL-17+ cells were significantly higher in PV lesions, compared to PF lesions and normal control skins, respectively (all P < 0.05). Moreover, the correlation between IL-23+ cells and IL-17+ cells was significant (r = 0.7546; P < 0.05). Taken together, our results provided evidence that the IL-23/IL-17 axis may play a crucial role in the immunopathogenesis of PV and may serve as novel therapeutic target for PV.
Figures

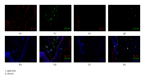
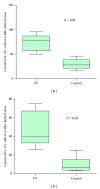

References
-
- Rizzo C, Fotino M, Zhang Y, Chow S, Spizuoco A, Sinha AA. Direct characterization of human T cells in pemphigus vulgaris reveals elevated autoantigen-specific Th2 activity in association with active disease. Clinical and Experimental Dermatology. 2005;30(5):535–540. - PubMed
-
- Yokoyama T, Amagai M. Immune dysregulation of pemphigus in humans and mice. Journal of Dermatology. 2010;37(3):205–213. - PubMed
-
- Amagai M, Klaus-Kovtun V, Stanley JR. Autoantibodies against a novel epithelial cadherin in Pemphigus vulgaris, a disease of cell adhesion. Cell. 1991;67(5):869–877. - PubMed
-
- Hertl M. Humoral and cellular autoimmunity in autoimmune bullous skin disorders. International Archives of Allergy and Immunology. 2000;122(2):91–100. - PubMed
-
- Satyam A, Khandpur S, Sharma VK, Sharma A. Involvement of TH1/TH2 cytokines in the pathogenesis of autoimmune skin diseasepemphigus vulgaris. Immunological Investigations. 2009;38(6):498–509. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

