Pharmacoinformatics elucidation of potential drug targets against migraine to target ion channel protein KCNK18
- PMID: 24899801
- PMCID: PMC4038526
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S63096
Pharmacoinformatics elucidation of potential drug targets against migraine to target ion channel protein KCNK18
Abstract
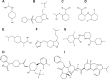
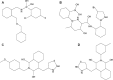
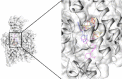
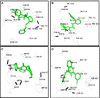
Migraine, a complex debilitating neurological disorder is strongly associated with potassium channel subfamily K member 18 (KCNK18). Research has emphasized that high levels of KCNK18 may be responsible for improper functioning of neurotransmitters, resulting in neurological disorders like migraine. In the present study, a hybrid approach of molecular docking and virtual screening were followed by pharmacophore identification and structure modeling. Screening was performed using a two-dimensional similarity search against recommended migraine drugs, keeping in view the physicochemical properties of drugs. LigandScout tool was used for exploring pharmacophore properties and designing novel molecules. Here, we report the screening of four novel compounds that have showed maximum binding affinity against KCNK18, obtained through the ZINC database, and Drug and Drug-Like libraries. Docking studies revealed that Asp-46, Ile-324, Ile-44, Gly-118, Leu-338, Val-113, and Phe-41 are critical residues for receptor-ligand interaction. A virtual screening approach coupled with docking energies and druglikeness rules illustrated that ergotamine and PB-414901692 are potential inhibitor compounds for targeting KCNK18. We propose that selected compounds may be more potent than the previously listed drug analogs based on the binding energy values. Further analysis of these inhibitors through site-directed mutagenesis could be helpful for exploring the details of ligand-binding pockets. Overall, the findings of this study may be helpful for designing novel therapeutic targets to cure migraine.
Keywords: KCNK18; TRESK; bioinformatics; migraine; modeling and docking; pharmacoinformatics; virtual screening.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pharmacoinformatic and molecular docking studies reveal potential novel antidepressants against neurodegenerative disorders by targeting HSPB8.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016 May 6;10:1605-18. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S101929. eCollection 2016. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016. PMID: 27226709 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive evolution and elucidating the potential inhibitor against schizophrenia to target DAOA (G72) isoforms.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Jul 3;9:3471-80. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S63946. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 26170631 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of 3 common polymorphisms in the KCNK18 gene in an Australian Migraine case-control cohort.Gene. 2013 Oct 10;528(2):343-6. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.07.030. Epub 2013 Jul 31. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23911303
-
Migraine: Role of the TRESK two-pore potassium channel.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011 Nov;43(11):1533-6. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2011.08.002. Epub 2011 Aug 9. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21855646 Review.
-
Ion channelopathies and migraine pathogenesis.Mol Genet Genomics. 2017 Aug;292(4):729-739. doi: 10.1007/s00438-017-1317-1. Epub 2017 Apr 7. Mol Genet Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28389699 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacoinformatics, Adaptive Evolution, and Elucidation of Six Novel Compounds for Schizophrenia Treatment by Targeting DAOA (G72) Isoforms.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:5925714. doi: 10.1155/2017/5925714. Epub 2017 Jan 19. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28197415 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacoinformatic and molecular docking studies reveal potential novel antidepressants against neurodegenerative disorders by targeting HSPB8.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016 May 6;10:1605-18. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S101929. eCollection 2016. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016. PMID: 27226709 Free PMC article.
-
Current Therapeutic Molecules and Targets in Neurodegenerative Diseases Based on in silico Drug Design.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018;16(6):649-663. doi: 10.2174/1570159X16666180315142137. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29542412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular docking analyses of CYP450 monooxygenases of Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) reveal synergism of quercetin with paraoxon and tetraethyl pyrophosphate: in vivo and in silico studies.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2020 May 9;9(3):212-221. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfaa023. eCollection 2020 Jun. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2020. PMID: 32670552 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting ion channels with ultra-large library screening for hit discovery.Front Mol Neurosci. 2024 Jan 5;16:1336004. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1336004. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38249296 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wolff H. Headache and Other Head Pain. New York: Oxford University Press; 1948.
-
- Hoskin KL, Kraube H, Goadsby PJ. Central activation of the trigeminovascular pathway in the cat is inhibited by dihydroergotamine. A c-Fos and electrophysiological study. Brain. 1996;119(1):249–256. - PubMed
-
- Limmroth V, May A, Auerbach P, Wosnitza G, Eppe T, Diener HC. Changes in cerebral blood flow velocity after treatment with sumatriptan or placebo and implications for the pathophysiology of migraine. J Neurol Sci. 1996;138(1–2):60–65. - PubMed
-
- Afridi SK, Matharu MS, Lee L, et al. A PET study exploring the laterality of brainstem activation in migraine using glyceryl trinitrate. Brain. 2005;128(Pt 4):932–939. - PubMed
-
- Kelman L. The triggers or precipitants of the acute migraine attack. Cephalalgia. 2007;27(5):394–402. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

