Detection and Characterization of Parathyroid Adenoma/Hyperplasia for Preoperative Localization: Comparison Between (11)C-Methionine PET/CT and (99m)Tc-Sestamibi Scintigraphy
- PMID: 24900103
- PMCID: PMC4035189
- DOI: 10.1007/s13139-013-0212-x
Detection and Characterization of Parathyroid Adenoma/Hyperplasia for Preoperative Localization: Comparison Between (11)C-Methionine PET/CT and (99m)Tc-Sestamibi Scintigraphy
Abstract
Purpose: (11)C-Methionine PET/CT (Met-PET/CT) is a useful imaging method for detection of parathyroid adenoma; however, the reported detection rate has been variable. The current study was intended to investigate detection sensitivity and preoperative localization of parathyroid adenoma (PA) or parathyroid hyperplasia (PH) on Met-PET/CT compared with (99m)Tc-sestamibi (MIBI) scintigraphy in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism (HPT) or suspected PA.
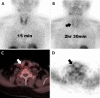
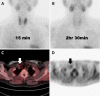
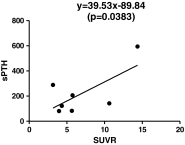
Methods: Met-PET/CT and MIBI scintigraphy images were reviewed by two nuclear medicine physicians unaware of pathologic results. Detection sensitivities and preoperative localization of detected parathyroid tissues into five predefined segments were evaluated by visual assessment and semi-quantitative analysis with ratio of standardized uptake values (SUVR) between parathyroid tissue and normal lung as reference. Linear regression analysis with SUVR and serum parathyroid hormone (sPTH) was performed for characterization of PA or PH. Predicted PTH (pPTH) was calculated and compared with sPTH in PH and PA. Each pPTH was obtained for a calculated SUVR by using linear regression model from the result of previous linear regression analysis between SUVR and sPTH.
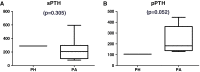
Results: In 16 patients, detection sensitivities of Met-PET/CT and MIBI scintigraphy were 91.7 % (11/12) and 41.7 % (5/12) for PA and PH including both biopsy-confirmed and clinically-suspected cases, and 100 % (8/8) and 50 % (4/8) for pathologically confirmed PA and PH cases only, respectively. Met-PET/CT showed higher performance than MIBI scintigraphy in localization of parathyroid tissues; correct localization rate was 87.5 % (7/8) on Met-PET/CT and 50 % (4/8) on MIBI scintigraphy. In semi-quantitative analysis, SUVR was linearly associated with sPTH by linear regression analysis (sPTH = 39.53 × SUVR - 89.84, p = 0.0383). There was a borderline significant difference in pPTH between PH and PA (35.1 vs 204.7 ± 164.0, p = 0.052), while there was no significant difference in sPTH between PH and PA (289 vs 230.4 ± 160.4, p = 0.305).
Conclusions: Met-PET/CT has a potential to be a useful diagnostic modality for preoperative detection and localization of parathyroid tissues with higher sensitivity than MIBI scintigraphy, and for characterization of PA or PH.
Keywords: 11C-methionine PET/CT; 99mTc-sestamibi scintigraphy; Parathyroid adenoma; Parathyroid hyperplasia; Preoperative localization; Primary hyperparathyroidism.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of 99mTc-sestamibi and 11C-methionine PET/CT in the localization of parathyroid adenomas in primary hyperparathyroidism.Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2014 Mar-Apr;33(2):93-8. doi: 10.1016/j.remn.2013.08.002. Epub 2013 Oct 11. Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2014. PMID: 24125595
-
Comparison between technetium-99m methoxyisobutylisonitrile scintigraphy and ultrasound in the diagnosis of parathyroid adenoma and parathyroid hyperplasia.Nucl Med Commun. 2018 Dec;39(12):1129-1137. doi: 10.1097/MNM.0000000000000921. Nucl Med Commun. 2018. PMID: 30239472 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison between 11C-methionine PET/CT and MIBI SPECT/CT for localization of parathyroid adenomas/hyperplasia.Nucl Med Commun. 2015 Jan;36(1):53-9. doi: 10.1097/MNM.0000000000000216. Nucl Med Commun. 2015. PMID: 25244350
-
[Localization of parathyroid adenomas with C11-methionine PET-CT].Chirurg. 2014 Jul;85(7):601-6. doi: 10.1007/s00104-013-2695-5. Chirurg. 2014. PMID: 24599386 Review. German.
-
Preoperative Localization for Primary Hyperparathyroidism: A Clinical Review.Biomedicines. 2021 Apr 6;9(4):390. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9040390. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 33917470 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Five-year Retrospective Study on Primary Hyperparathyroidism in South India: Emerging Roles of Minimally Invasive Parathyroidectomy and Preoperative Localization with Methionine Positron Emission Tomography-Computed Tomography Scan.Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2018 May-Jun;22(3):355-361. doi: 10.4103/ijem.IJEM_445_16. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2018. PMID: 30090727 Free PMC article.
-
11C-methionine PET/CT and conventional imaging techniques in the diagnosis of primary hyperparathyroidism.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023 Apr 1;13(4):2352-2363. doi: 10.21037/qims-22-584. Epub 2023 Feb 16. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023. PMID: 37064353 Free PMC article.
-
The value of SPECT/CT in localizing pain site and prediction of treatment response in patients with chronic low back pain.J Korean Med Sci. 2014 Dec;29(12):1711-6. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2014.29.12.1711. Epub 2014 Nov 21. J Korean Med Sci. 2014. PMID: 25469075 Free PMC article.
-
Is C-11 Methionine PET/CT Able to Localise Sestamibi-Negative Parathyroid Adenomas?World J Surg. 2017 Apr;41(4):980-985. doi: 10.1007/s00268-016-3795-4. World J Surg. 2017. PMID: 27834016
-
Head-to-head comparison of [11C]methionine PET, [11C]choline PET, and 4-dimensional CT as second-line scans for detection of parathyroid adenomas in primary hyperparathyroidism.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2024 Mar;51(4):1050-1059. doi: 10.1007/s00259-023-06488-7. Epub 2023 Nov 17. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2024. PMID: 37975887 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Taillefer R. Tc-99m sestamibi parathyroid scintigraphy. In: Freeman LM, editor. Nuclear Medicine Annual 1995. New York: Raven Press; 1995. p. 51–79.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
