Difference of clinical and radiological characteristics according to radioiodine avidity in pulmonary metastases of differentiated thyroid cancer
- PMID: 24900139
- PMCID: PMC4035156
- DOI: 10.1007/s13139-013-0239-z
Difference of clinical and radiological characteristics according to radioiodine avidity in pulmonary metastases of differentiated thyroid cancer
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate differences in clinical, radiological and laboratory findings between pulmonary metastasis with and without radioiodine avidity in thyroidectomized differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) patients with pulmonary metastasis who underwent high-dose I-131 treatment.
Methods: A total of 105 DTC patients with pulmonary metastasis (age, 48.7 ± 16.8 years; women/men, 78/27) were included. Clinical characteristics, chest computed tomography (CT), F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (F-18 FDG PET)/CT and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)-stimulated serum thyroglobulin (s-Tg) level were compared between patients with and without radioiodine uptake in metastatic lung lesions. The response to I-131 treatment was evaluated with follow-up study.
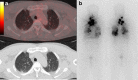
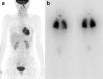
Results: Eighty-nine patients (84.8 %, whole-body scan positive [WBSP] group) showed radioiodine uptake at pulmonary metastasis on post I-131 treatment whole-body scan (WBS) and 16 patients (15.2 %, WBS negative [WBSN] group) did not show uptake at pulmonary lesions on the WBS. Ninety percent and 87 % of the WBSP group had visible metastatic lesions on CT and F-18 FDG PET/CT; however, all of the patients in the WBSN group showed lesions on CT and F-18 FDG PET/CT. In seven (6.7 %) of 105 patients, CT and F-18 FDG PET/CT could not detect pulmonary lesions, which were diagnosed by post I-131 treatment WBS. Complete disease remission was achieved in six (5.7 %) patients and all of them were in the WBSP group.
Conclusions: Metastatic lesion was not visualized on chest CT or F-18 FDG PET/CT in 6.7 % of DTC patients with pulmonary metastasis and the lesion was visualized only on post I-131 treatment WBS. Complete remission was achieved in 5.7 % of DTC patients with pulmonary metastasis and the cured metastases were non-visualizing or micronodular lesions on chest CT and demonstrated radioiodine avidity on post I-131 treatment WBS.
Keywords: Differentiated thyroid cancer; I-131 treatment; Pulmonary metastasis; Radioiodine avidity.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
