Expression patterns of glucose transporter-1 gene and thyroid specific genes in human papillary thyroid carcinoma
- PMID: 24900148
- PMCID: PMC4028475
- DOI: 10.1007/s13139-013-0249-x
Expression patterns of glucose transporter-1 gene and thyroid specific genes in human papillary thyroid carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: The expression of glucose transporter-1 (Glut-1) gene and those of major thyroid-specific genes were examined in papillary carcinoma tissues, and the expressions of these genes were compared with cancer differentiation grades.
Materials and methods: Twenty-four human papillary carcinoma tissues were included in this study. The expressions of Glut-1- and thyroid-specific genes [sodium/iodide symporter (NIS), thyroid peroxidase, thyroglobulin, TSH receptor and pendrin] were analyzed by RT-PCR. Expression levels were expressed as ratios versus the expression of beta-actin. Pathologic differentiation of papillary carcinoma was classified into a relatively well-differentiated group (n = 13) and relatively less differentiated group (n = 11).
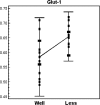
Results: Glut-1 gene expression was significantly higher in the less differentiated group (0.66 ± 0.04) than in the well-differentiated group (0.59 ± 0.07). The expression levels of the NIS, PD and TG genes were significantly higher in the well-differentiated group (NIS: 0.67 ± 0.20, PD: 0.65 ± 0.21, TG: 0.74 ± 0.16) than in the less differentiated group (NIS: 0.36 ± 0.05, PD: 0.49 ± 0.08, TG: 0.60 ± 0.11), respectively. A significant negative correlation was found between Glut-1 and NIS expression, and positive correlations were found between NIS and TG, and between NIS and PD.
Conclusion: The NIS, PD and TG genes were highly expressed in well-differentiated thyroid carcinomas, whereas the Glut-1 gene was highly expressed in less differentiated thyroid carcinomas. These findings provide a molecular rationale for the management of papillary carcinoma, especially in the selection of FDG PET or radioiodine whole-body scan and I-131-based therapy.
Keywords: Glucose transporter-1; Papillary thyroid cancer; Pendrin; Sodium/iodide symporter; TSH receptor; Thyroglobulin; Thyroid peroxidase.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Expression of the Na+/I- symporter gene in human thyroid tumors: a comparison study with other thyroid-specific genes.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999 Sep;84(9):3228-34. doi: 10.1210/jcem.84.9.5996. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999. PMID: 10487692
-
Expressions of human sodium iodide symporter mRNA in primary and metastatic papillary thyroid carcinomas.Thyroid. 2000 Mar;10(3):211-7. doi: 10.1089/thy.2000.10.211. Thyroid. 2000. PMID: 10779135
-
Relations Between Pathological Markers and Radioiodine Scan and (18)F-FDG PET/CT Findings in Papillary Thyroid Cancer Patients With Recurrent Cervical Nodal Metastases.Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015 Jun;49(2):127-34. doi: 10.1007/s13139-015-0324-6. Epub 2015 Feb 13. Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015. PMID: 26085858 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium/iodide symporter: a key transport system in thyroid cancer cell metabolism.Eur J Endocrinol. 1999 Nov;141(5):443-57. doi: 10.1530/eje.0.1410443. Eur J Endocrinol. 1999. PMID: 10576759 Review.
-
Iodide handling disorders (NIS, TPO, TG, IYD).Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017 Mar;31(2):195-212. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2017.03.006. Epub 2017 Apr 4. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017. PMID: 28648508 Review.
Cited by
-
Radio-Iodide Treatment: From Molecular Aspects to the Clinical View.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 27;13(5):995. doi: 10.3390/cancers13050995. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33673669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic reprogramming and its clinical application in thyroid cancer.Oncol Lett. 2019 Aug;18(2):1579-1584. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10485. Epub 2019 Jun 18. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31423225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FDG PET/CT for the early prediction of RAI therapy response in patients with metastatic differentiated thyroid carcinoma.PLoS One. 2019 Jun 25;14(6):e0218416. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218416. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31237886 Free PMC article.
-
[18F]FDG Uptake and Expression of Immunohistochemical Markers Related to Glycolysis, Hypoxia, and Proliferation in Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules.Mol Imaging Biol. 2023 Jun;25(3):483-494. doi: 10.1007/s11307-022-01776-4. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Mol Imaging Biol. 2023. PMID: 36253663 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
HER inhibitor promotes BRAF/MEK inhibitor-induced redifferentiation in papillary thyroid cancer harboring BRAFV600E.Oncotarget. 2017 Mar 21;8(12):19843-19854. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15773. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28423638 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Taurog A. Hormone synthesis. In: Braverman LE, Utigen RD eds. The thyroid: a fundamental and clinical text. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven; 1996: p. 47–81.
-
- Chung JK, Lee YJ, Kim C, et al. Mechanism related to [18 F]fluorodeoxyglucose uptake of human colon cancers transplanted in nude mice. J Nucl Med. 1999;40:339–346. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
