Optimization of Pharmacokinetics through Manipulation of Physicochemical Properties in a Series of HCV Inhibitors
- PMID: 24900257
- PMCID: PMC4018142
- DOI: 10.1021/ml200163b
Optimization of Pharmacokinetics through Manipulation of Physicochemical Properties in a Series of HCV Inhibitors
Abstract
A novel series of HCV replication inhibitors based on a pyrido[3,2-d]pyrimidine core were optimized for pharmacokinetics (PK) in rats. Several associations between physicochemical properties and PK were identified and exploited to guide the design of compounds. In addition, a simple new metric that may aid in the prediction of bioavailability for compounds with higher polar surface area is described (3*HBD-cLogP).
Keywords: 3*HBD-cLogP; HCV inhibitors; Pharmacokinetics; pyrido[3,2-d]pyrimidine core.
Figures
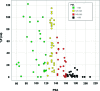



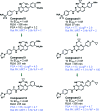






References
-
- Lipinski C. A.; Lombardo F.; Dominy B. W.; Feeney P. J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 1997, 23, 4–25. - PubMed
-
- Veber D. F.; Johnson S. R.; Cheng H.-Y.; Smith B. R.; Ward K. W.; Kopple K. D. Molecular Properties That Influence the Oral Bioavailability of Drug Candidates. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 2615–2623. - PubMed
-
- Leeson P. D.; Davis A. M. Time-Related Differences in the Physical Property Profiles of Oral Drugs. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 6338–6348. - PubMed
-
- Johnson T. W.; Dress K. R.; Edwards M. Using the Golden Triangle to Optimize Clearance and Oral Absorption. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 5560–5564. - PubMed
-
- Hou T.; Wang J.; Zhang W.; Xu X. ADME Evaluation in Drug Discovery. 7. Prediction of Oral Absorption by Correlation and Classification. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2007, 47, 208–218. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

